-
This work tabulates measured and derived values of coefficients for Lorentz
and CPT violation in the Standard-Model Extension. Summary tables are extracted
listing maximal attained sensitivities in the matter, photon, neutrino, and
gravity sectors. Tables presenting definitions and properties are also
compiled.
-
The claim that the large scale structure of the Universe is hierarchical has
a very long history going back at least to Charlier's papers of the early 20th
century. In recent years, the debate has centered largely on the works of Sylos
Labini, Joyce, Pietronero and others, who have made the quantative claim that
the large scale structure of the Universe is quasi-fractal with fractal
dimension D≈2. There is now a concensus that this is the case on
medium scales, with the main debate revolving around what happens on the scales
of the largest available modern surveys.
This paper, which is a realization of a worldview which is deeply rooted in
the ideas of Leibniz and Mach shows, as a very special case of a general
formalism, that such a fractal D≈2 world is necessarily a world of
dynamical equilibrium.
We use the cosmology to write down a simple galaxy model as an arbitrary
spherically symmetric bounded perturbation of the D≈2 equilibrium
environment. A necessary mass continuity condition on the perturbation boundary
between galactic interior and the exterior environment immediately defines that
boundary as a critical acceleration boundary with a0∼4πGΣF
where a0 is the critical acceleration parameter and ΣF is the
characteristic mass surface density of the D≈2 fractal environment.
The MOND acceleration condition V20/R0=a0 for circular orbits on the
critical boundary follows in a straightforward manner.
-
This article investigates the full Boltzmann equation up to second order in
the cosmological perturbations. Describing the distribution of polarized
radiation by a tensor valued distribution function, we study the gauge
dependence of the distribution function and summarize the construction of the
gauge-invariant distribution function. The Liouville operator which describes
the free streaming of electrons, and the collision term which describes the
scattering of photons on free electrons are computed up to second order.
Finally, the remaining dependence in the direction of the photon momentum is
handled by expanding in projected symmetric trace-free multipoles and also in
the more commonly used normal modes components. The results obtained remain to
be used for computing numerically the contribution in the cosmic microwave
background bispectrum which arises from the evolution of second order
perturbations, in order to disentangle the primordial non-Gaussianity from the
one generated by the subsequent non-linear evolution.
-
Spectroscopic observations of a solar limb flare recorded by SUMER on SOHO
reveal, for the first time, hot fast magnetic reconnection outflows in the
corona. As the reconnection site rises across the SUMER spectrometer slit,
significant blue- and red-shift signatures are observed in sequence in the Fe
XIX line, reflecting upflows and downflows of hot plasma jets, respectively.
With the projection effect corrected, the measured outflow speed is between
900-3500 km/s, consistent with theoretical predictions of the Alfvenic outflows
in magnetic reconnection region in solar impulsive events. Based on theoretic
models, the magnetic field strength near the reconnection region is estimated
to be 19-37 Gauss.
-
Jet physics is again flourishing as a result of Chandra's ability to resolve
high-energy emission from the radio-emitting structures of active galaxies and
separate it from the X-ray-emitting thermal environments of the jets. These
enhanced capabilities have coincided with an increasing interest in the link
between the growth of super-massive black holes and galaxies, and an
appreciation of the likely importance of jets in feedback processes. I review
the progress that has been made using Chandra and XMM-Newton observations of
jets and the medium in which they propagate, addressing several important
questions, including: Are the radio structures in a state of minimum energy? Do
powerful large-scale jets have fast spinal speeds? What keeps jets collimated?
Where and how does particle acceleration occur? What is jet plasma made of?
What does X-ray emission tell us about the dynamics and energetics of radio
plasma/gas interactions? Is a jet's fate determined by the central engine?
-
(Abridged) We describe here the most ambitious survey currently planned in
the optical, the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST). A vast array of
science will be enabled by a single wide-deep-fast sky survey, and LSST will
have unique survey capability in the faint time domain. The LSST design is
driven by four main science themes: probing dark energy and dark matter, taking
an inventory of the Solar System, exploring the transient optical sky, and
mapping the Milky Way. LSST will be a wide-field ground-based system sited at
Cerro Pach\'{o}n in northern Chile. The telescope will have an 8.4 m (6.5 m
effective) primary mirror, a 9.6 deg2 field of view, and a 3.2 Gigapixel
camera. The standard observing sequence will consist of pairs of 15-second
exposures in a given field, with two such visits in each pointing in a given
night. With these repeats, the LSST system is capable of imaging about 10,000
square degrees of sky in a single filter in three nights. The typical 5σ
point-source depth in a single visit in r will be ∼24.5 (AB). The
project is in the construction phase and will begin regular survey operations
by 2022. The survey area will be contained within 30,000 deg2 with
δ<+34.5∘, and will be imaged multiple times in six bands, ugrizy,
covering the wavelength range 320--1050 nm. About 90\% of the observing time
will be devoted to a deep-wide-fast survey mode which will uniformly observe a
18,000 deg2 region about 800 times (summed over all six bands) during the
anticipated 10 years of operations, and yield a coadded map to r∼27.5. The
remaining 10\% of the observing time will be allocated to projects such as a
Very Deep and Fast time domain survey. The goal is to make LSST data products,
including a relational database of about 32 trillion observations of 40 billion
objects, available to the public and scientists around the world.
-
The designation of the customary restricted three-body disturbing potential
Φ as the perturbation Hamiltonian is believed to be the cause of Neptune
ring arcs' radial offset between theories and observations. To identify the
appropriate perturbation Hamiltonian, the energy integral in the fixed frame of
a restricted three-body system, consisting of the central, primary, and test
bodies, is reconsidered. It is shown that the perturbation energy includes the
disturbing potential Φ and the potential arising from the angular momentum
terms of the test body. Both potentials happen to be singular as the test body
goes to infinity contradicting to the perturbation nature. These two potentials
can be combined to an energy relevant disturbing potential Φ∗=βΦ
which is regular at infinity because of the cancellation of the singularities.
For circular orbits of the primary, the energy equation is conservative, and
Φ∗ is identified as the perturbation Hamiltonian. Applying this result
to evaluate the backgrund effect of Triton to the arc-Galatea system of
Neptune, it is shown that there is a small difference
ΔΦ=(Φ∗−Φ) which amounts to an outward radial offset of the
corotation location of Galatea by 0.3 Km. The mismatch between the pattern
speed of Galatea's corotation potential and the mean motion velocity of the
arcs could be resolved by considering the finite mass of Fraternite. However,
by using Φ∗, Galatea's eccentricity could be reassessed in terms of the
mass of Fraternite.
-
We analyze in details the standard Primordial Nucleosynthesis scenario. In
particular we discuss the key theoretical issues which are involved in a
detailed prediction of light nuclide abundances, as the weak reaction rates,
neutrino decoupling and nuclear rate modeling. We also perform a new analysis
of available data on the main nuclear processes entering the nucleosynthesis
reaction network, with particular stress on their uncertainties as well as on
their role in determining the corresponding uncertainties on light nuclide
theoretical estimates. The current status of theoretical versus experimental
results for 2H, 3He, 4He and 7Li is then discussed using the determination of
the baryon density as obtained from Cosmic Microwave Background anisotropies.
-
Orbital detectors without pointing capability have to keep their field of
view axis laying on their orbital plane, to observe the largest sky fraction. A
general approach to estimate the exposure of each sky element for such
detectors is a valuable tool in the R&D phase of a project, when the detector
characteristics are still to be fixed. An analytical method to estimate the sky
exposure is developed, which makes only few very reasonable approximations. The
formulae obtained with this method are used to compute the histogram of the sky
exposure of a hypothetical gamma-ray detector installed on the ISS. The C++
code used in this example is freely available on the
https://github.com/dcasadei/SkyCoverage web page.
-
In this paper we establish a generally and globally valid coordinate system
in curved space-time with the simultaneous hypersurface orthogonal to the time
coordinate. The time coordinate can be preseted according to practical evolving
process and keep synchronous with the evolution of the realistic world. In this
coordinate system, it is convenient to express the physical laws and to
calculate physical variables with clear geometrical meaning. We call it
"natural coordinate system". The constructing method for the natural coordinate
system is concretely provided, and its physical and geometrical meanings are
discussed in detail. In NCS we make classical approximation of spinor equation
to get Newtonian mechanics, and then make weak field approximation of
Einstein's equation and low speed approximation of particles moving in the
space-time. From the analysis and examples we find it is a nice coordinate
system to describe the realistic curved space-time, and is helpful to
understand the nature of space-time.
-
We constructed the magnetic field oscillation model (hereafter the MO model)
by analogizing the periodically reversing phenomenon of the solar magnetic
field to pulsars. Almost all kinds of pulsar radiation phenomena are best
explained using the MO model, especially polarization characteristics, glitch,
generation rate, the geodetic precession of pulsars and the configuration of
pulsar-wind nebula of the Crab. The MO model also provides satisfactory
explanation for other characteristics of pulsars, e.g., interpulse, spin-down,
pulse nulling, beat and pulse drift, the loss rate of the rotating energy, and
the accuracy of frequency. We present eight verification methods for the MO
model. In addition to pulsars, our MO model can also be used to explain the
pulse emission from non-compact stars such as the ultracool dwarf TVLM
513-46546 and the magnetic chemically peculiar star CU Virginis.
-
In cosmology, the cosmic curvature K and the cosmological constant
Λ are two important parameters, and the values have strong influence on
the behavior of the universe. In the context of normal cosmology, under the
ordinary assumptions of positive mass-energy and initial negative pressure, we
find the initial singularity of the universe is certainly absent and we have
K=1. This means total spatial structure of the universe should be a
3-dimensional sphere S3. For the cyclic cosmological model, we have
Λ≲. Obviously, such constraints would be
helpful for the researches on the properties of dark matter and dark energy in
cosmology.
-
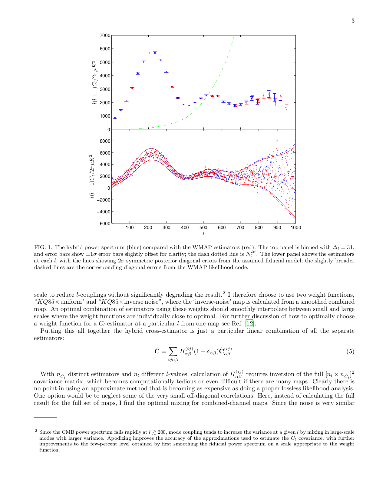
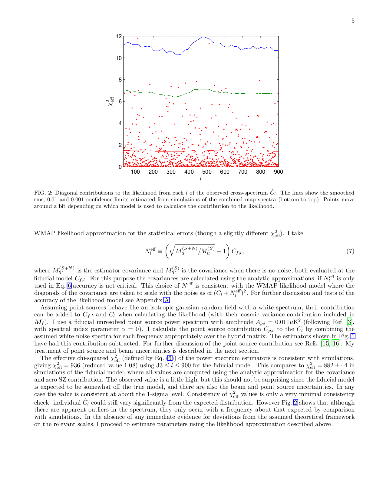
I calculate a hybrid cross-power spectrum estimator from the WMAP 5-year CMB
temperature maps, discuss the goodness of fit, and then constrain cosmological
parameters. The spectrum and results are generally consistent with previous
results, though the power spectrum error bars are slightly smaller and there
are small shifts at high ell. The small improvement in error bars is obtained
at very low numerical cost but does not significantly improve parameter
constraints. I discuss the accuracy of the likelihood model and how constraints
on the optical depth translate into constraints on the reionization history
allowing for helium reionization. In the appendices I propose a simple
reionization parameterization that determines the history in terms of a
mid-point reionization redshift, and suggest a new likelihood approximation for
chi-squared-like distributions with varying skewness.
-
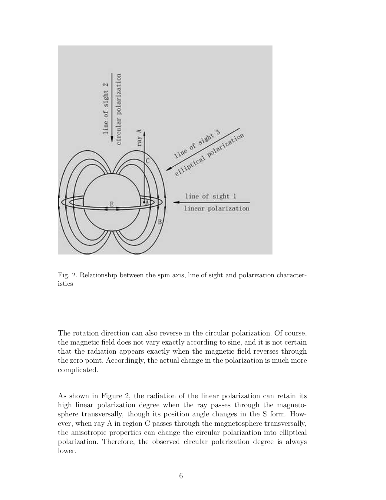
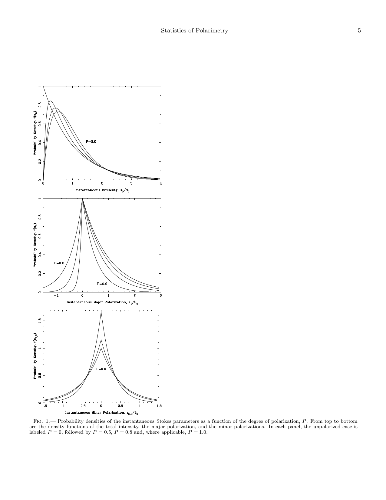
A four-dimensional statistical description of electromagnetic radiation is
developed and applied to the analysis of radio pulsar polarization. The new
formalism provides an elementary statistical explanation of the modal
broadening phenomenon in single pulse observations. It is also used to argue
that the degree of polarization of giant pulses has been poorly defined in past
studies. Single and giant pulse polarimetry typically involves sources with
large flux densities and observations with high time resolution, factors that
necessitate consideration of source-intrinsic noise and small-number
statistics. Self noise is shown to fully explain the excess polarization
dispersion previously noted in single pulse observations of bright pulsars,
obviating the need for additional randomly polarized radiation. Rather, these
observations are more simply interpreted as an incoherent sum of covariant,
orthogonal, partially polarized modes. Based on this premise, the
four-dimensional covariance matrix of the Stokes parameters may be used to
derive mode-separated pulse profiles without any assumptions about the
intrinsic degrees of mode polarization. Finally, utilizing the small-number
statistics of the Stokes parameters, it is established that the degree of
polarization of an unresolved pulse is fundamentally undefined; therefore,
previous claims of highly polarized giant pulses are unsubstantiated.
Unpublished supplementary material is appended after the bibliography.
-
The southwestern (SW) part of the Galactic H II region M17 contains an
obscured ionization front that is most easily seen at infrared and radio
wavelengths. It is nearly edge-on, thus offering an excellent opportunity to
study the way in which the gas changes from fully ionized to molecular as
radiation from the ionizing stars penetrates into the gas. M17 is also one of
the very few H II regions for which the magnetic field strength can be measured
in the photodissociation region ( PDR) that forms the interface between the
ionized and molecular gas. Here we model an observed line of sight through the
gas cloud, including the H+, H0 (PDR), and molecular layers, in a fully
self-consistent single calculation. An interesting aspect of the M17 SW bar is
that the PDR is very extended. We show that the strong magnetic field that is
observed to be present inevitably leads to a very deep PDR, because the
structure of the neutral and molecular gas is dominated by magnetic pressure,
rather than by gas pressure, as previously had been supposed.We also show that
a wide variety of observed facts can be explained if a hydrostatic geometry
prevails, in which the gas pressure from an inner X-ray hot bubble and the
outward momentum of the stellar radiation field compress the gas and its
associated magnetic field in the PDR, as has already been shown to occur in the
Orion Nebula. The magnetic field compression may also amplify the local
cosmic-ray density. The pressure in the observed magnetic field balances the
outward forces, suggesting that the observed geometry is a natural consequence
of the formation of a star cluster within a molecular cloud.
-
A new method of matrix template matching is presented in the context of
pulsar timing analysis. Pulse arrival times are typically measured using only
the observed total intensity light curve. The new technique exploits the
additional timing information available in the polarization of the pulsar
signal by modeling the transformation between two polarized light curves in the
Fourier domain. For a number of millisecond pulsars, arrival time estimates
derived from polarimetric data are predicted to exhibit greater precision and
accuracy than those derived from the total intensity alone. Furthermore, the
transformation matrix produced during template matching may be used to
calibrate observations of other point sources. Unpublished supplementary
material is appended after the bibliography.
-
The big bang began with a cold dark matter shell and a hot core undergoing
nucleosynthesis due to particle localization. The Planck spectrum CBR was
generated from standing radiation and highly conducting walls. Its energy level
was well below antimatter production. The flatness of universe geometry was due
to a bounce. The well correlated galaxies originated from cold shell matter
capturing the hot core gases. All matter well above the supranuclear range will
violate the equivalence principle and lose gravitation. All black holes (no
singularities) lose gravitational energy and have caused dark energy.
-
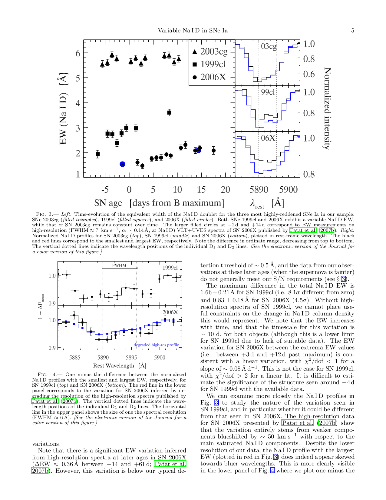
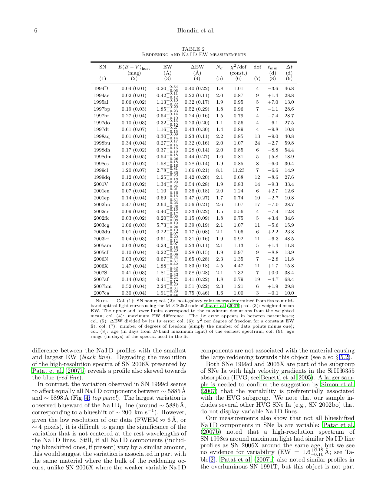
(Original) Recent high-resolution spectra of the Type Ia SN 2006X have
revealed the presence of time-variable and blueshifted Na I D features,
interpreted by Patat et al. as originating in circumstellar material within the
progenitor system. The variation seen in SN 2006X induces relatively large
changes in the total Na I D equivalent width (\Delta\rm{EW}\approx 0.5
\unicode{x212B} in just over two weeks), that would be detectable at lower
resolutions. We have used a large data set comprising 2400 low-resolution
spectra of 450 Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia) obtained by the CfA Supernova
Program to search for variable Na I D features. Out of the 31 SNe Ia (including
SN 2006X) in which we could have detected similar EW variations, only one other
(SN 1999cl) shows variable Na I D features, with an even larger change over a
similar ~10-day timescale (\Delta\rm{EW} = 1.66 \pm 0.21 \unicode{x212B}).
Interestingly, both SN 1999cl and SN 2006X are the two most highly-reddened
objects in our sample, raising the possibility that the variability is
connected to dusty environments.
(Erratum) The large variation in the Na I D equivalent width observed in SN
1999cl results in fact from a measurement error. Our new measurements show that
the EW variation is significantly lower, at 0.43 \pm 0.14 \unicode{x212B}.
While the EW variation remains statistically significant (3.1\sigma different
from zero), it is now below the detection threshold of 0.5 \unicode{x212B}
derived from the Monte Carlo simulations published in the original paper. As a
result, SN 1999cl should no longer be considered as an object displaying
variable Na I D lines in our study. The fraction of SNe Ia in our sample
displaying Na I D lines thus goes from \sim6% (2/31) in the original study to
\sim3% (1/31) in the revised analysis, SN 2006X being the only SN Ia in our
sample with variable Na I D lines.
-
A connection between fractal dimensions of "turbulent facets" and fractal
dimensions in diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) is shown. The theoretical
correspondence is elucidated and an empirical support to the above claim is
given.
-
These notes provide an introduction to the theory of the formation and early
evolution of planetary systems. Topics covered include the structure, evolution
and dispersal of protoplanetary disks; the formation of planetesimals,
terrestrial and gas giant planets; and orbital evolution due to gas disk
migration, planetesimal scattering, planet-planet interactions, and tides.
-
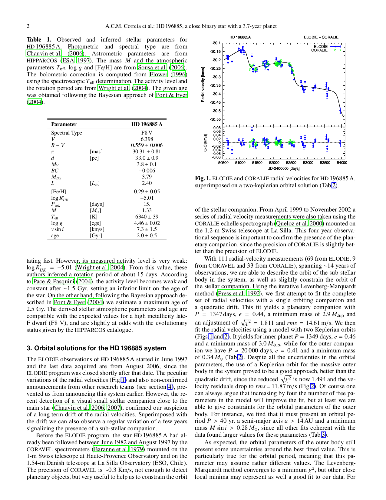
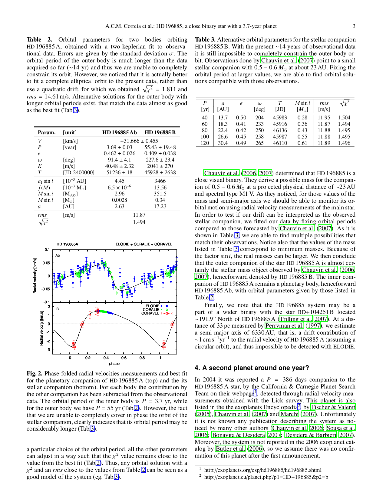
In this letter we report the possible existence of a second planet in the
transiting extrasolar planet system HD 17156 and its interactive dynamics with
the previously known planet. The analysis is achieved through the \POFP\
optimization software which is based on a full integration of the system's
multiple-body Newtonian equations of motion. The two-planet solution yields a
significantly improved fit to the previously published radial velocities. The
two planets are strongly interacting and exchange angular momentum in a 5:1
mean motion resonance, yet remain stable as they mutually excite orbital
eccentricities and periastron advances.
-
The body of work presented here revolves around the investigation of the
existence and nature of extra-solar planetary systems. The fitting of stellar
radial velocity time series data is attempted by constructing a model to
quantify the orbital properties of a star-planetary system. This is achieved
with the Planetary Orbit Fitting Process (POFP). Though specific to the
investigated problem, the POFP is founded on two separate, more general ideas.
One is a Solver producing the gravitational dynamics of a Three-Body system by
integrating its Newtonian equations of motion. The other is an independent
optimisation scheme. Both have been devised using MATLAB. Applying the
optimisation to the Solver results in a realistic Three-Body dynamics that best
describes the radial velocity data under the model-specific
orbital-observational constraints. Combining these aspects also allows for the
study of dynamical instability derived from interaction, which is reaffirmed as
a necessary criterion for evaluating the fit. The validity of POFP solutions
with respect to the observations and other models is discussed in this context.
The underlying generality and fundamental principles demonstrate a larger frame
of operation where problems in Physics and Mathematics can be solved with a
multitude of techniques.
-
Aims:We aim to significantly increase the number of detected extra-solar
planets in a magnitude-limited sample to improve our knowledge of their orbital
element distributions and thus obtain better constraints for planet-formation
models.
Methods: Radial-velocity data were taken at Haute-Provence Observatory (OHP,
France) with the ELODIE echelle spectrograph.
Results: We report the presence of a planet orbiting HD 196885 A, with an
orbital period of 1349 days. This star was previously suggested to host a 386
-day planet, but we cannot confirm its existence. We also detect the presence
of a stellar companion, HD 196885 B, and give some constraints on its orbit.
-
The possible time variation of dimensionless fundamental constants of nature,
such as the fine-structure constant \alpha, is a legitimate subject of
physical enquiry. By contrast, the time variation of dimensional constants,
such as \hbar, c, G, e, k,... which are merely human constructs whose
number and values differ from one choice of units to the next, has no
operational meaning. To illustrate this, we refute a recent claim of Davies et
al that black holes can discriminate between two contending theories of varying
\alpha, one with varying c and the other with varying e. In Appendix A we
respond to criticisms by P. Davies and two Nature referees. In Appendix B we
respond to remarks by Magueijo and by T. Davis. In Appendix C we critique
recent claims by Copi, A. Davis and Krauss to have placed constraints on
\Delta G/G.} In Appendix D we provide extracts of a lecture by Dirac, of
which we have only recently become aware, which includes the comment "Talking
about whether a thing is constant or not does not have any absolute meaning
unless that quantity is dimensionless".
-
A pedagogical introduction to aspects of string cosmology, including the
landscape (BPBT) solution to the cosmological constant problem, brane-antibrane
inflation, warped compactification, the KKLMMT model, the eta problem of SUGRA
models, DBI inflation, Kahler modulus and racetrack inflation, the D3-D7 model,
cosmic superstrings, and the problem of reheating. Also includes basic methods
for phenomenology of multifield models with nonstandard kinetic terms.