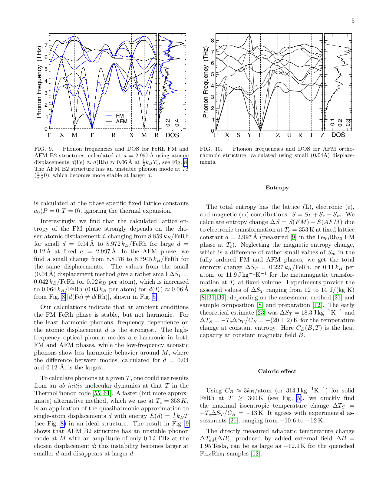
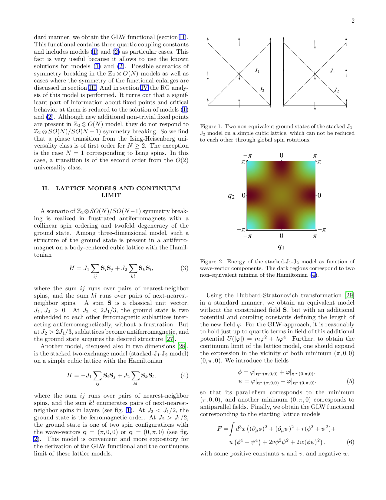
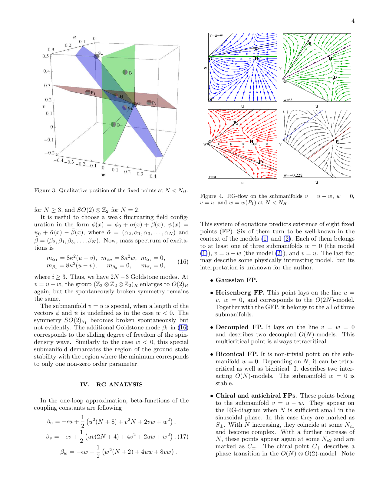
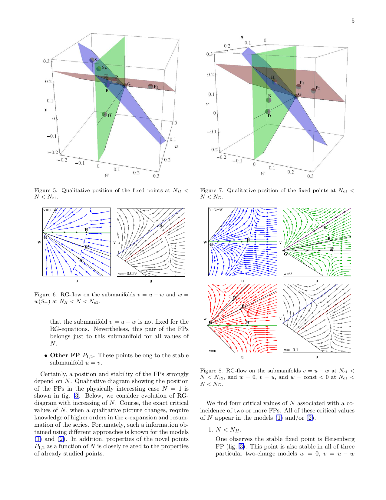
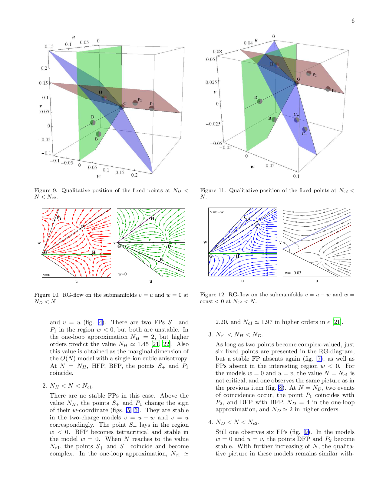
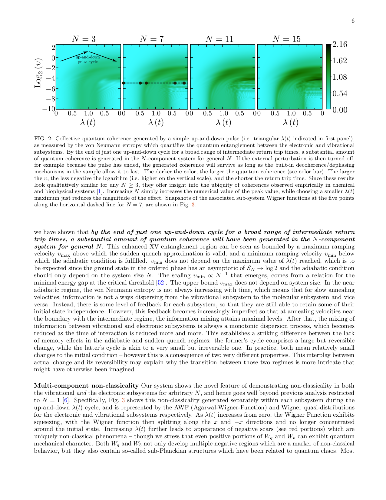
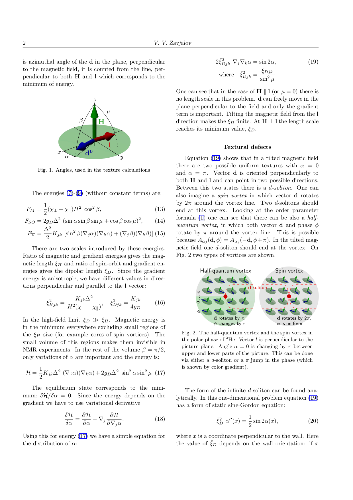
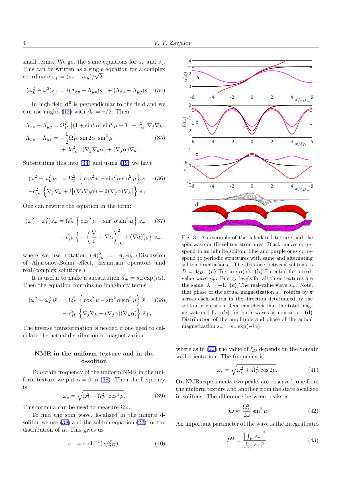
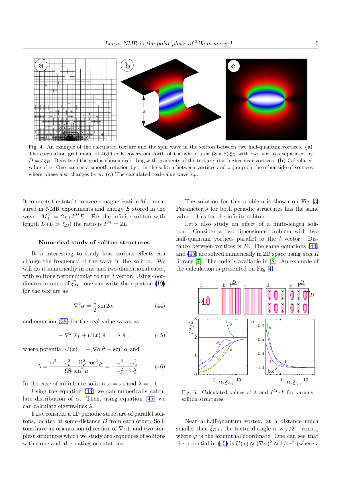
-
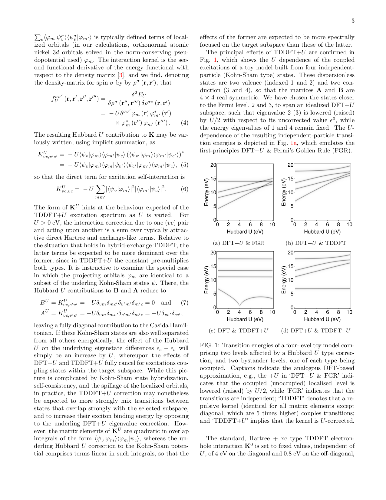
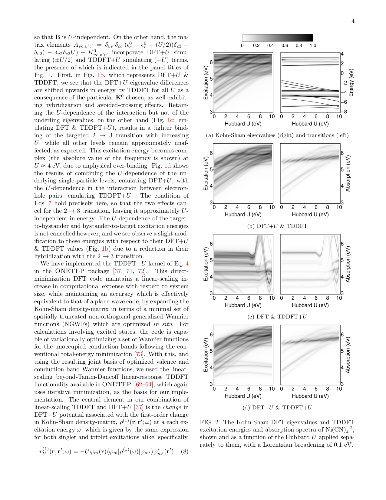
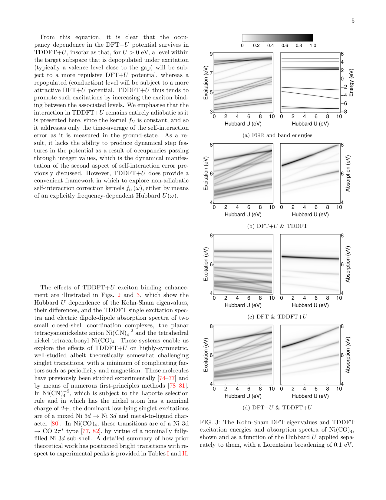
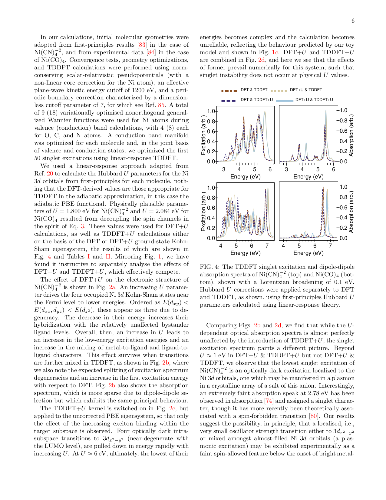
We develop a generalization of the Kohn-Sham density functional theory
(KS-DFT) + Hubbard U (DFT+U) method to the excited-state regime. This has
the form of Hubbard U corrected linear-response time-dependent DFT, or
`TDDFT+U'. Combined with calculated linear-response Hubbard U parameters,
it may provide a computationally light, first-principles method for the
simulation of tightly-bound excitons on transition-metal ions. Our presented
implementation combines linear-scaling DFT+U and linear-scaling TDDFT, but
the approach is broadly applicable. In detailed benchmark tests on two
Ni-centred diamagnetic coordination complexes with variable U values, it is
shown that the Hubbard U correction to an approximate adiabatic semi-local
exchange-correlation interaction kernel lowers the excitation energies of
transitions exclusively within the targeted localized subspace, by increasing
the exciton binding of the corresponding electron-hole pairs. This partially
counteracts the Hubbard U correction to the exchange-correlation potential in
KS-DFT, which increases excitation energies into, out of, and within the
targeted localised subspace by modifying the underlying KS-DFT eigenspectrum.
This compensating effect is most pronounced for optically dark transitions
between localized orbitals of the same angular momentum, for which experimental
observation may be challenging and theoretical approaches are at their most
necessary. Overall, our results point to shortcomings in the contemporary
DFT+U corrective potential, either in its functional form, or when applied to
transition-metal orbitals but not to ligand ones, or both.
-
We consider cycles for graded C∗,r-algebras (Real C∗-algebras)
which are compatible with the ∗-structure and the real structure. Their
characters are cyclic cocycles. We define a Connes type pairing between such
characters and elements of the van Daele K-groups of the C∗,r-algebra
and its real subalgebra. This pairing vanishes on elements of finite order. We
define a second type of pairing between characters and K-group elements which
is derived from a unital inclusion of C∗-algebras. It is potentially
non-trivial on elements of order two and torsion valued. Such torsion valued
pairings yield topological invariants for insulators. The two-dimensional
Kane-Mele and the three-dimensional Fu-Kane-Mele strong invariant are special
cases of torsion valued pairings. We compute the pairings for a simple class of
periodic models and establish structural results for two dimensional aperiodic
models with odd time reversal invariance.
-
Using coherent states as initial states, we investigate the quantum dynamics
of the Lipkin-Meshkov-Glick (LMG) and Dicke models in the semi-classical limit.
They are representative models of bounded systems with one- and two-degrees of
freedom, respectively. The first model is integrable, while the second one has
both regular and chaotic regimes. Our analysis is based on the survival
probability. Within the regular regime, the energy distribution of the initial
coherent states consists of quasi-harmonic sub-sequences of energies with
Gaussian weights. This allows for the derivation of analytical expressions that
accurately describe the entire evolution of the survival probability, from
t=0 to the saturation of the dynamics. The evolution shows decaying
oscillations with a rate that depends on the anharmonicity of the spectrum and,
in the case of the Dicke model, on interference terms coming from the
simultaneous excitation of its two-degrees of freedom. As we move away from the
regular regime, the complexity of the survival probability is shown to be
closely connected with the properties of the corresponding classical phase
space. Our approach has broad applicability, since its central assumptions are
not particular of the studied models.
-
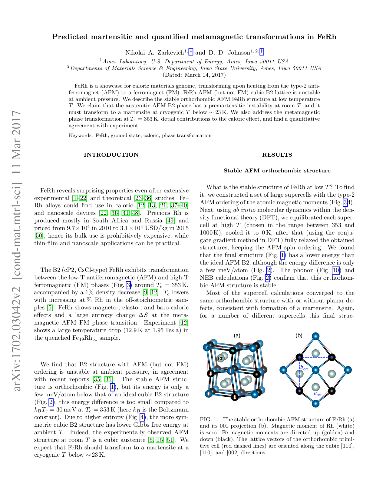
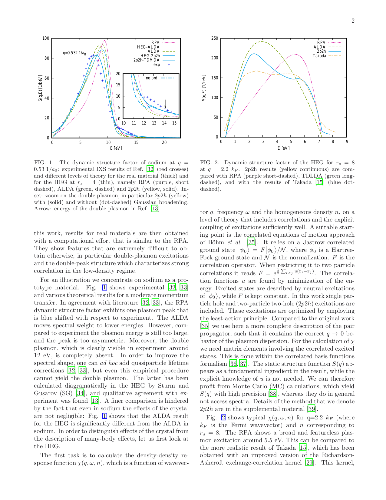
Reversible, diffusionless, first-order solid-solid phase transitions
accompanied by caloric effects are critical for applications in the solid-state
cooling and heat-pumping devices. Accelerated discovery of caloric materials
requires reliable but faster estimators for predictions and high-throughput
screening of system-specific dominant caloric contributions. We assess
reliability of the computational methods that provide thermodynamic properties
in relevant solid phases at or near a phase transition. We test the methods
using the well-studied B2 FeRh alloy as a "fruit fly" in such a materials
genome discovery, as it exhibits a metamagnetic transition which generates
multicaloric (magneto-, elasto-, and baro-caloric) responses. For lattice
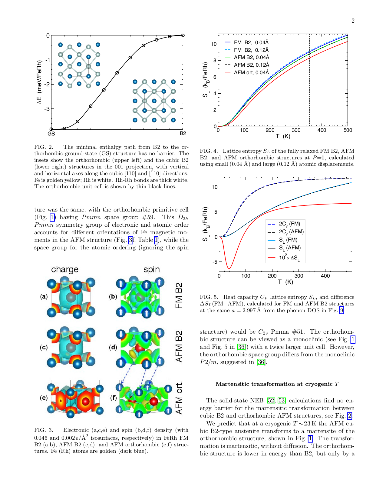
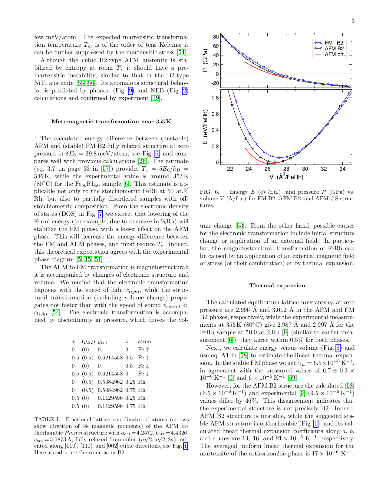
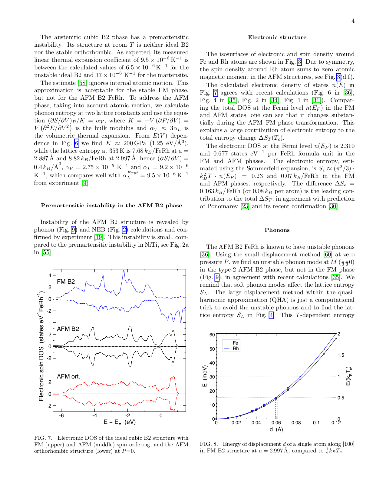
entropy contributions, we find that the commonly-used linear-response and
small-displacement phonon methods are invalid near instabilities that arise
from the anharmonicity of atomic potentials, and we offer a more reliable and
precise method for calculating lattice entropy at a fixed temperature. Then, we
apply a set of reliable methods and estimators to the metamagnetic transition
in FeRh (predicted 346±12 K, observed 353±1 K) and calculate the
associated caloric properties, such as isothermal entropy and isentropic
temperature changes.
-
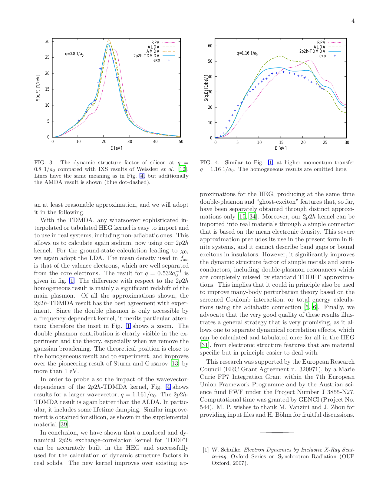
The charge-density response of extended materials is usually dominated by the
collective oscillation of electrons, the plasmons. Beyond this feature,
however, intriguing many-body effects are observed. They cannot be described by
one of the most widely used approaches for the calculation of dielectric
functions, which is time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) in the
adiabatic local density approximation (ALDA). Here we propose an approximation
to the TDDFT exchange-correlation kernel which is non-adiabatic and non-local.
It is derived in the homogeneous electron gas and implemented in the real
system in a simple mean density approximation. This kernel contains effects
that are completely absent in the ALDA; in particular, it correctly describes
the double plasmon in the dynamic structure factor of sodium, and it shows the
characteristic low-energy peak that appears in systems with low electronic
density. It also leads to an overall quantitative improvement of spectra.
-
In the present course, an overview is presented of the fundamentals of
continuum-polaron physics, which provide the basis of the analysis of polaron
effects in ionic crystals and polar semiconductors. These Lecture Notes deal
with "large", or "continuum", polarons, as described by the Fr\"ohlich
Hamiltonian. The emphasis is on the polaron optical absorption, with detailed
mathematical derivations.
-
We calculate the fluorescence spectra of a driven lattice of coupled
cavities. To do this, we extend methods of evaluating two-time correlations in
infinite lattices to open quantum systems; this allows access to momentum
resolved fluorescence spectrum. We illustrate this for a driven-dissipative
transverse field anisotropic XY model. By studying the fluctuation dissipation
theorem, we find the emergence of a quasi-thermalized steady state with a
temperature dependent on system parameters; for blue detuned driving, we show
this effective temperature is negative. In the low excitation density limit, we
compare these numerical results to analytical spin-wave theory, providing an
understanding of the form of the distribution function and the origin of
quasi-thermalization.
-
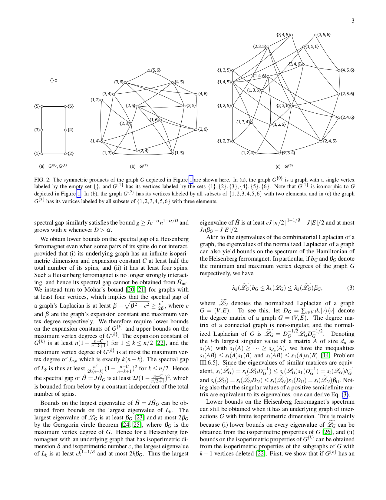
We give a polynomial-time algorithm for computing upper bounds on some of the
smaller energy eigenvalues in a spin-1/2 ferromagnetic Heisenberg model with
any graph G for the underlying interactions. An important ingredient is the
connection between Heisenberg models and the symmetric products of G. Our
algorithms for computing upper bounds are based on generalized diameters of
graphs. Computing the upper bounds amounts to solving the minimum assignment
problem on G, which has well-known polynomial-time algorithms from the field
of combinatorial optimization. We also study the possibility of computing the
lower bounds on some of the smaller energy eigenvalues of Heisenberg models.
This amounts to estimating the isoperimetric inequalities of the symmetric
product of graphs. By using connections with discrete Sobolev inequalities, we
show that this can be performed by considering just the vertex-induced
subgraphs of G. If our conjecture for a polynomial time approximation
algorithm to solve the edge-isoperimetric problem holds, then our proposed
method of estimating the energy eigenvalues via approximating the
edge-isoperimetric properties of vertex-induced subgraphs will yield a
polynomial time algorithm for estimating the smaller energy eigenvalues of the
Heisenberg ferromagnet.
-
Inserting a magnetic flux into a two-dimensional one-particle Hamiltonian
leads to a spectral flow through a given gap which is equal to the Chern number
of the associated Fermi projection. This paper establishes a generalization to
higher even dimension by inserting non-abelian monopoles of the Wu-Yang type.
The associated spectral flow is then equal to a higher Chern number. For the
study of odd spacial dimensions, a new so-called `chirality flow' is introduced
which, for the insertion of a monopole, is then linked to higher winding
numbers. This latter fact follows from a new index theorem for the spectral
flow between two unitaries which are conjugates of each other by a self-adjoint
unitary.
-
We present an alternative one-electron equation for resolving many-electron
problem to one-electron approximation and including the exchange and
correlation effects in an analytical way, thereby fulfilling the requirements
for ab initio calculation. To derive one-electron equation, we accept a new
notion of equivalent function suggestive of the pseudo wavefunction. As a
result, we reduce many-electron equation to one-electron including the exchange
effect in an analytical method. Moreover we accept the notion of phase norm for
two electrons to resolve the electronic correlation problem. The phase norm is
used to specify the electron-approachable limit between particles. We take into
consideration the electronic correlation with the help of a correlation-hole
function in terms of the phase norm, by which multiplying the integrand of the
operator term representing the interaction between electrons. Using the phase
norm leads to analytical consideration of the electronic correlation without
employing in a factitious way the additional term pertaining to correlation, so
it embodies the physical essence of electronic correlation. The derived
equation becomes an one-electron equation which does not include an additional
term pertaining to the exchange and correlation, but takes into consideration
the exchange and correlation effects in a rigorous ab initio way.
-
A non-Hermitian complex symmetric 2x2 matrix toy model is used to study
projective Hilbert space structures in the vicinity of exceptional points
(EPs). The bi-orthogonal eigenvectors of a diagonalizable matrix are
Puiseux-expanded in terms of the root vectors at the EP. It is shown that the
apparent contradiction between the two incompatible normalization conditions
with finite and singular behavior in the EP-limit can be resolved by
projectively extending the original Hilbert space. The complementary
normalization conditions correspond then to two different affine charts of this
enlarged projective Hilbert space. Geometric phase and phase jump behavior are
analyzed and the usefulness of the phase rigidity as measure for the distance
to EP configurations is demonstrated. Finally, EP-related aspects of
PT-symmetrically extended Quantum Mechanics are discussed and a conjecture
concerning the quantum brachistochrone problem is formulated.
-
Critical behavior of three-dimensional classical frustrated antiferromagnets
with a collinear spin ordering and with an additional twofold degeneracy of the
ground state is studied. We consider two lattice models, whose continuous limit
describes a single phase transition with a symmetry class differing from the
class of non-frustrated magnets as well as from the classes of magnets with
non-collinear spin ordering. A symmetry breaking is described by a pair of
independent order parameters, which are similar to order parameters of the
Ising and O(N) models correspondingly. Using the renormalization group method,
it is shown that a transition is of first order for non-Ising spins. For Ising
spins, a second order phase transition from the universality class of the O(2)
model may be observed. The lattice models are considered by Monte Carlo
simulations based on the Wang-Landau algorithm. The models are a ferromagnet on
a body-centered cubic lattice with the additional antiferromagnetic exchange
interaction between next-nearest-neighbor spins and an antiferromagnet on a
simple cubic lattice with the additional interaction in layers. We consider the
cases N=1,2,3 and in all of them find a first-order transition. For the N=1
case we exclude possibilities of the second order or pseudo-first order of a
transition. An almost second order transition for large N is also discussed.
-
We analyze the topological Z2 invariant, which characterizes time
reversal invariant topological insulators, in the framework of index theory and
K-theory. The topological Z2 invariant counts the parity of
generalized Majorana zero modes, which can be interpreted as an analytical
index. As we show, it fits perfectly into a mod 2 index theorem, and the
topological index provides an efficient way to compute the topological
Z2 invariant. Finally, we give a new version of the bulk-boundary
correspondence which yields an alternative explanation of the index theorem and
the topological Z2 invariant. Here the boundary is not the
geometric boundary of a probe, but an effective boundary in the momentum space.
-
The ability to prepare a physical system in a desired quantum state is
central to many areas of physics such as nuclear magnetic resonance, cold
atoms, and quantum computing. Yet, preparing states quickly and with high
fidelity remains a formidable challenge. In this work we implement cutting-edge
Reinforcement Learning (RL) techniques and show that their performance is
comparable to optimal control methods in the task of finding short,
high-fidelity driving protocol from an initial to a target state in
non-integrable many-body quantum systems of interacting qubits. RL methods
learn about the underlying physical system solely through a single scalar
reward (the fidelity of the resulting state) calculated from numerical
simulations of the physical system. We further show that quantum state
manipulation, viewed as an optimization problem, exhibits a spin-glass-like
phase transition in the space of protocols as a function of the protocol
duration. Our RL-aided approach helps identify variational protocols with
nearly optimal fidelity, even in the glassy phase, where optimal state
manipulation is exponentially hard. This study highlights the potential
usefulness of RL for applications in out-of-equilibrium quantum physics.
-
To gain control over magnetic order on ultrafast time scales, a fundamental
understanding of the way electron spins interact with the surrounding crystal
lattice is required. However, measurement and analysis even of basic collective
processes such as spin-phonon equilibration have remained challenging. Here, we
directly probe the flow of energy and angular momentum in the model insulating
ferrimagnet yttrium iron garnet. Following ultrafast resonant lattice
excitation, we observe that magnetic order reduces on distinct time scales of 1
ps and 100 ns. Temperature-dependent measurements, a spin-coupling analysis and
simulations show that the two dynamics directly reflect two stages of
spin-lattice equilibration. On the 1-ps scale, spins and phonons reach
quasi-equilibrium in terms of energy through phonon-induced modulation of the
exchange interaction. This mechanism leads to identical demagnetization of the
ferrimagnet's two spin-sublattices and a novel ferrimagnetic state of increased
temperature yet unchanged total magnetization. Finally, on the much slower,
100-ns scale, the excess of spin angular momentum is released to the crystal
lattice, resulting in full equilibrium. Our findings are relevant for all
insulating ferrimagnets and indicate that spin manipulation by phonons,
including the spin Seebeck effect, can be extended to antiferromagnets and into
the terahertz frequency range.
-
Gravitons possess a Berry curvature due to their helicity. We derive the
semiclassical equations of motion for gravitons taking into account the Berry
curvature. We show that this quantum correction leads to the splitting of the
trajectories of right- and left-handed gravitational waves in curved space, and
that this correction can be understood as a topological phenomenon. This is the
spin Hall effect (SHE) of gravitational waves. We find that the SHE of
gravitational waves is twice as large as that of light. Possible future
observations of the SHE of gravitational waves can potentially test the quantum
nature of gravitons beyond the classical general relativity.
-
We give a topological classification of quantum walks on an infinite 1D
lattice, which obey one of the discrete symmetry groups of the tenfold way,
have a gap around some eigenvalues at symmetry protected points, and satisfy a
mild locality condition. No translation invariance is assumed. The
classification is parameterized by three indices, taking values in a group,
which is either trivial, the group of integers, or the group of integers modulo
2, depending on the type of symmetry. The classification is complete in the
sense that two walks have the same indices if and only if they can be connected
by a norm continuous path along which all the mentioned properties remain
valid. Of the three indices, two are related to the asymptotic behaviour far to
the right and far to the left, respectively. These are also stable under
compact perturbations. The third index is sensitive to those compact
perturbations which cannot be contracted to a trivial one. The results apply to
the Hamiltonian case as well. In this case all compact perturbations can be
contracted, so the third index is not defined. Our classification extends the
one known in the translation invariant case, where the asymptotic right and
left indices add up to zero, and the third one vanishes, leaving effectively
only one independent index. When two translationally invariant bulks with
distinct indices are joined, the left and right asymptotic indices of the
joined walk are thereby fixed, and there must be eigenvalues at 1 or −1
(bulk-boundary correspondence). Their location is governed by the third index.
We also discuss how the theory applies to finite lattices, with suitable
homogeneity assumptions.
-
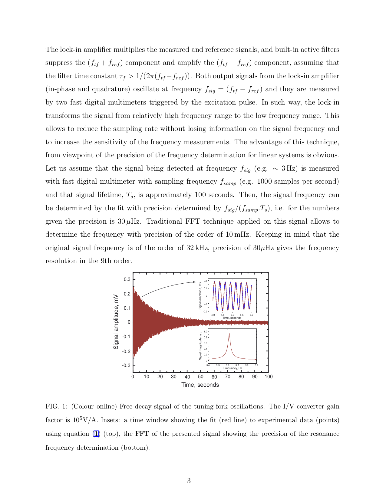
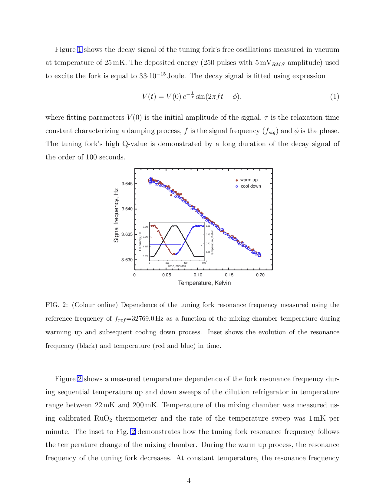
We present the experimental results on the spontaneous emergence of the phase
coherence in the system of oscillating electric dipoles in quartz
piezo-resonators caused by the van der Waals interaction. Spontaneous emergence
of the phase coherence in these systems is manifested via
temperature-dependent, extremely accurate tune-up of their resonance
frequencies in 9th order with relative spectral line-width δf0/f0
less than 3.10−8 (this number is comparable with that in lasers) along
with the very high frequency stability characterized by the low values of the
Allan deviations. We also show that the application of an incoherent (noise)
excitation signal leads to a spontaneous formation of the phase coherent state,
and that the dissipation processes do not affect this phase coherent state
(i.e. the resonance frequency of the system). All above-mentioned signatures
are typical characteristics for a Bose-Einstein condensate of excitations.
Smallness of the relative spectral lime-width in quartz piezo-resonators opens
their potential application as alternative time etalons.
-
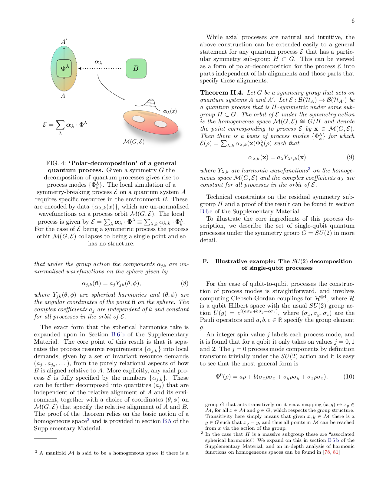
What is the structure of general quantum processes on composite systems that
respect a global or local symmetry principle? How does the irreversible use of
quantum resources behave under such symmetry principles? Here we employ an
information-theoretic framework to address these questions and show that every
symmetric quantum process on a system has a highly rigid decomposition in terms
of the flow of symmetry-breaking degrees of freedom between each subsystem and
its environment. The decomposition has a natural causal structure that can be
represented diagrammatically and makes explicit gauge degrees of freedom
between subsystems. The framework also provides a novel quantum information
perspective on lattice gauge theories and a method to gauge general quantum
processes beyond Lagrangian formulations. This procedure admits a simple
resource-theoretic interpretation, and thus offers a natural context in which
features such as information flow and entanglement in gauge theories and
quantum thermodynamics could be studied. The framework also provides a flexible
toolkit with which to analyse the structure of general quantum processes. As an
application, we make use of a `polar decomposition' for quantum processes to
discuss the repeatable use of quantum resources and to provide a novel
perspective in terms of the coordinates induced on the orbit of a local process
under a symmetry action.
-
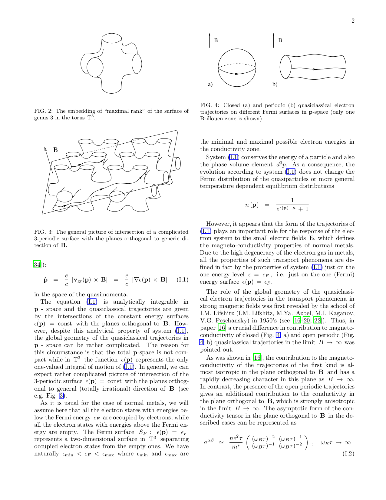
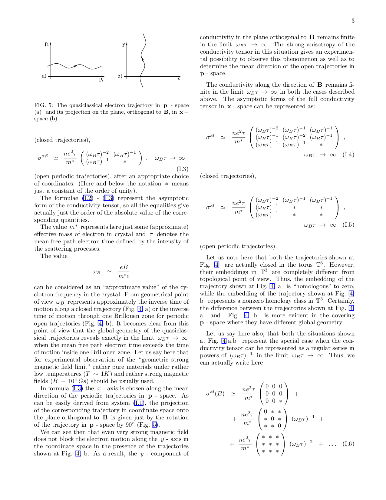
We consider the electric conductivity in normal metals in presence of a
strong magnetic field. It is assumed here that the Fermi surface of a metal has
rather complicated form such that different types of quasiclassical electron
trajectories can appear on the Fermi level for different directions of B. The
effects we consider are connected with the existence of regular (stable) open
electron trajectories which arise in general on complicated Fermi surfaces. The
trajectories of this type have a nice geometric description and represent
quasiperiodic lines with a fixed mean direction in the p-space. Being stable
geometric objects, the trajectories of this kind exist for some open regions in
the space of directions of B, which can be represented by "Stability Zones" on
the unit sphere. The main goal of the paper is to give a description of the
analytical behavior of conductivity in the Stability Zones, which demonstrates
in general rather nontrivial properties.
-
Based on the microscopic Maxwell equations, we develop a method of
description of the electric field in a spontaneously polarized isotropic
nonpolar dielectric. We find the solution for the electric field
E(r) for several typical examples. Moreover, we generalize
Helmholtz's formula for the electric force acting on a volume element of a
dielectric with regard for the contribution of the spontaneous polarization.
-
In this paper, we show that the Laughlin wave function is a Hamiltonian and
its associated Berry connection as the Schr\"odinger equation by transforming
the Schr\"odinger equation into the Kirchhoff equation which describes the
evolution of n point vortices in Hydrodynamics. This helps us to view the
Berry connection associated with Laughlin wave function or Schr\"odinger
equation is not Hermitian, therefore we propose a self adjoint model
Hamiltonian for the fractional quantum Hall effect, from the study of Kirchhoff
equation, using superymmetric quantum mechanics whose solutions are complex
Hermite polynomials. The Schr\"odinger equation as Berry connection allows us
to formulate the problem of quantisation in terms of topology, as the quantum
numbers are topological invariant which arise due to singularities in the
Kirchhoff equation. Quantisation arises as it continuously connects the
topologically inequivalent Hamiltonians in the Hilbert space.
-
Contribution to thermal conductivity from conduction electron scattering on
crystal field magnetic excitations is calculated and analyzed for normal
rare-earth inter-metallic paramagnets. It is shown that in temperatures much
lower than Debye temperature \TD its behavior essentially depends on the
ground state of magnetic ion in crystal field and on the excitation energy in
relation to \TD\,. Combined effect from the electron scattering on the
crystal-field excitations, on acoustic phonons, and on nonmagnetic impurities
is discussed in reference to CF splitting character and to the relative
intensities of magnetic and non-magnetic scattering. Total thermal conductivity
resulting from these three sources of scattering is calculated for REIn3
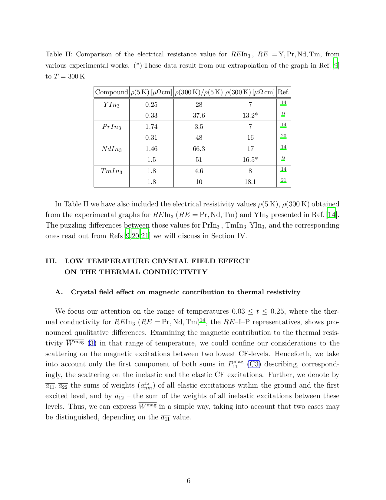
(RE=Nd,\,Pr,\,Tm) and compared with experimental data.
-
We show that a pulsed stimulus can be used to generate many-body quantum
coherences in light-matter systems of general size. Specifically, we calculate
the exact real-time evolution of a driven, generic out-of-equilibrium system
comprising an arbitrary number N qubits coupled to a global boson field. A
novel form of dynamically-driven quantum coherence emerges for general N and
without having to access the empirically challenging strong-coupling regime.
Its properties depend on the speed of the changes in the stimulus.
Non-classicalities arise within each subsystem that have eluded previous
analyses. Our findings show robustness to losses and noise, and have potential
functional implications at the systems level for a variety of nanosystems,
including collections of N atoms, molecules, spins, or superconducting qubits
in cavities -- and possibly even vibration-enhanced light harvesting processes
in macromolecules.
-
3He is an example of the system with non-trivial Cooper paring. A few
different superfluid phases are known in this system. Recently the new one, the
polar phase, have been observed in 3He confined in nematically ordered
aerogel. A number of various topological defects including half-quantum
vortices can exist the polar phase. In this work we present theoretical and
numerical studies of linear NMR in the polar phase both in the uniform
order-parameter texture and in the presence of half-quantum vortices.