-
This paper studies fractional integral operator for vector fields in weighted
L1. Using the estimates on fractional integral operator and Stein-Weiss
inequalities, we can give a new proof for a class of Caffarelli-Kohn-Nirenberg
inequalities and establish new \divg-\curl inequalities for vector fields.
-
A new, extended nonlinear framework of the ordinary real analysis
incorporating a novel concept of {\em duality structure} and its applications
into various nonlinear dynamical problems is presented. The duality structure
is an asymptotic property that should affect the late time asymptotic behaviour
of a nonlinear dynamical system in a nontrivial way leading naturally to
signatures generic to a complex system. We argue that the present formalism
would offer a natural framework to understand the abundance of complex systems
in natural, biological, financial and related problems. We show that the power
law attenuation of a dispersive, lossy wave equation, conventionally deduced
from fractional calculus techniques, could actually arise from the present
asymptotic duality structure. Differentiability on a Cantor type fractal set is
also formulated.
-
We develop in this work a general version of paracontrolled calculus that
allows to treat analytically within this paradigm some singular partial
differential equations with the same efficiency as regularity structures. This
work deals with the analytic side of the story and offers a toolkit for the
study of such equations, under the form of a number of continuity results for
some operators. We illustrate the efficiency of this elementary approach on the
examples of the 3-dimensional generalised parabolic Anderson model equation and
the generalised KPZ equation driven by a (1+1)-dimensional space/time white
noise.
-
The sine process is a rigid point process on the real line, which means that
for almost all configurations X, the number of points in an interval I=[−R,R] is determined by the points of X outside of I. In addition, the
points in I are an orthogonal polynomial ensemble on I with a weight
function that is determined by the points in X∖I. We prove a
universality result that in particular implies that the correlation kernel of
the orthogonal polynomial ensemble tends to the sine kernel as the length
|I|=2R tends to infinity, thereby answering a question posed by A.I. Bufetov.
-
Let P(N) be the power set of N. We say that a
function μ∗:P(N)→R is an upper density if, for
all X,Y⊆N and h,k∈N+, the following hold: (F1)
μ∗(N)=1; (F2) μ∗(X)≤μ∗(Y) if X⊆Y;
(F3) μ∗(X∪Y)≤μ∗(X)+μ∗(Y); (F4) μ∗(k⋅X)=1kμ∗(X), where k⋅X:={kx:x∈X}; (F5)
μ∗(X+h)=μ∗(X).
We show that the upper asymptotic, upper logarithmic, upper Banach, upper
Buck, upper Polya, and upper analytic densities, together with all upper
α-densities (with α a real parameter ≥−1), are upper
densities in the sense of our definition. Moreover, we establish the mutual
independence of axioms (F1)-(F5), and we investigate various properties of
upper densities (and related functions) under the assumption that (F2) is
replaced by the weaker condition that μ∗(X)≤1 for every
X⊆N.
Overall, this allows us to extend and generalize results so far independently
derived for some of the classical upper densities mentioned above, thus
introducing a certain amount of unification into the theory.
-
We prove a global well-posedness result for the Landau-Lifshitz equation with
Gilbert damping provided that the BMO semi-norm of the initial data is small.
As a consequence, we deduce the existence of self-similar solutions in any
dimension. In the one-dimensional case, we characterize the self-similar
solutions associated with an initial data given by some (S2-valued)
step function and establish their stability. We also show the existence of
multiple solutions if the damping is strong enough. Our arguments rely on the
study of a dissipative quasilinear Schr\"odinger obtained via the stereographic
projection and techniques introduced by Koch and Tataru.
-
The article is concerned with polynomials g(x) whose graphs are "partially
packed" between two horizontal tangent lines. We assume that most of the local
maximum points of g(x) are on the first horizontal line, and most of the
local minimum points on the second horizontal line, except several
"exceptional" maximum or minimum points, that locate above or under two lines,
respectively. In addition, the degree of g(x) is exactly the number of all
extremum points +1. Then we call g(x) a multipartite Chebyshev polynomial
associated with the two lines. Under a certain condition, we show that g(x)
is expressed as a composition of the Chebyshev polynomial and a polynomial
defined by the x-component data of the exceptional extremum points of g(x)
and the intersection points of g(x) and the two lines. Especially, we study
in detail bipartite Chebyshev polynomials, which has only one exceptional
point, and treat a connection between such polynomials and elliptic integrals.
-
In this work, a generalization of pre-Gr\"{u}ss inequality is established.
Several bounds for the difference between two \v{C}eby\v{s}ev functional are
proved.
-
This is a draft of my textbook on mathematical analysis and the areas of
mathematics on which it is based. The idea is to fill the gaps in the existing
textbooks. Any remarks from readers are welcome.
-
This article studies sufficient conditions on families of approximating
kernels which provide N--term approximation errors from an associated
nonlinear approximation space which match the best known orders of N--term
wavelet expansion. These conditions provide a framework which encompasses some
notable approximation kernels including splines, so-called cardinal functions,
and many radial basis functions such as the Gaussians and general
multiquadrics. Examples of such kernels are given to justify the criteria, and
some computational experiments are done to demonstrate the theoretical results.
Additionally, the techniques involved allow for some new results on N--term
interpolation of Sobolev functions via radial basis functions.
-
We give a complete classification of analytic equivalence of germs of
parametric families of systems of complex linear differential equations
unfolding a generic resonant singularity of Poincare rank 1 in dimension n=2 whose leading matrix is a Jordan bloc. The moduli space of analytic
equivalence classes is described in terms of a tuple of formal invariants and a
single analytic invariant obtained from the trace of monodromy, and analytic
normal forms are given. We also explain the underlying phenomena of confluence
of two simple singularities and of a turning point, the associated Stokes
geometry, and the change of order of Borel summability of formal solutions in
dependence on a complex parameter.
-
In this paper, we derive systems of ordinary differential equations (ODEs)
satisfied by modular forms of level three, which are level three versions of
Ramanujan's system of ODEs satisfied by the classical Eisenstein series.
-
We obtain a two weight local Tb theorem for any elliptic and gradient
elliptic fractional singular integral operator T on the real line, and any pair
of locally finite positive Borel measures on the line. This includes the
Hilbert transform and in a sense improves on the T1 theorem by the authors and
M. Lacey.
-
In this article, we address pointwise sparse domination for multilinear
Calder\'on-Zygmund operators on upper doubling, geometrically doubling metric
measure spaces. As a consequence, we have obtained sharp quantitative weighted
estimates for multilinear Calder\'on-Zygmund operators.
-
The Whittaker-Shannon-Kotel'nikov (WSK) sampling theorem provides a
reconstruction formula for the bandlimited signals. In this paper, a novel kind
of the WSK sampling theorem is established by using the theory of quaternion
reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces. This generalization is employed to obtain
the novel sampling formulas for the bandlimited quaternion-valued signals. A
special case of our result is to show that the 2D generalized prolate
spheroidal wave signals obtained by Slepian can be used to achieve a sampling
series of cube-bandlimited signals. The solutions of energy concentration
problems in quaternion Fourier transform are also investigated.
-
Let C be a compact convex subset of Rn, f:C→R be a
convex function, and m∈{1,2,...,∞}. Assume that, along with f,
we are given a family of polynomials satisfying Whitney's extension condition
for Cm, and thus that there exists F∈Cm(Rn) such that
F=f on C. It is natural to ask for further (necessary and sufficient)
conditions on this family of polynomials which ensure that F can be taken to
be convex as well. We give a satisfactory solution to this problem in the case
m=∞, and also less satisfactory solutions in the case of finite m≥2 (nonetheless obtaining an almost optimal result for C a finite
intersection of ovaloids). For a solution to a similar problem in the case
m=1 (even for C not necessarily convex), see arXiv:1507.03931,
arXiv:1706.09808, arXiv:1706.02235.
-
The quaternion Fourier transform (QFT), a generalization of the classical 2D
Fourier transform, plays an increasingly active role in particular signal and
colour image processing. There tends to be an inordinate degree of interest
placed on the properties of QFT. The classical convolution theorem and
multiplication formula are only suitable for 2D Fourier transform of
complex-valued signal, and do not hold for QFT of quaternion-valued signal. The
purpose of this paper is to overcome these problems and establish the
Plancherel and inversion theorems of QFT in the square integrable signals space
L2. First, we investigate the behaviours of QFT in the integrable signals space
L1. Next, we deduce the energy preservation property which extends functions
from L1 to L2 space. Moreover, some other important properties such as modified
multiplication formula are also analyzed for QFT.
-
Athanasiadis conjectured that, for every positive integer r, the local
h-polynomial of the rth edgewise subdivision of any simplex has only real
zeros. In this paper, based on the theory of interlacing polynomials, we prove
that a family of polynomials related to the desired local h-polynomial is
interlacing and hence confirm Athanasiadis' conjecture.
-
This paper is devoted to a generalization of a Hadamard type inequality for
the permanent of a complex square matrix. Our proof is based on a non-trivial
extension of a technique used in Carlen, Lieb and Loss (Methods and
Applications of Analysis 13 (1) (2006) 1-17). We give an application to
coefficients of products of linear forms and show some auxiliary inequalities,
which might be of independent interest.
-
For data sampled from an arbitrary density on a manifold embedded in
Euclidean space, the Continuous k-Nearest Neighbors (CkNN) graph construction
is introduced. It is shown that CkNN is geometrically consistent in the sense
that under certain conditions, the unnormalized graph Laplacian converges to
the Laplace-Beltrami operator, spectrally as well as pointwise. It is proved
for compact (and conjectured for noncompact) manifolds that CkNN is the unique
unweighted construction that yields a geometry consistent with the connected
components of the underlying manifold in the limit of large data. Thus CkNN
produces a single graph that captures all topological features simultaneously,
in contrast to persistent homology, which represents each homology generator at
a separate scale. As applications we derive a new fast clustering algorithm and
a method to identify patterns in natural images topologically. Finally, we
conjecture that CkNN is topologically consistent, meaning that the homology of
the Vietoris-Rips complex (implied by the graph Laplacian) converges to the
homology of the underlying manifold (implied by the Laplace-de Rham operators)
in the limit of large data.
-
We prove in this note one weight norm inequalities for some positive
Bergman-type operators.
-
In this paper, we develop via real variable methods various characterisations
of the Hardy spaces in the multi-parameter flag setting. These
characterisations include those via, the non-tangential and radial maximal
function, the Littlewood--Paley square function and area integral, Riesz
transforms and the atomic decomposition in the multi-parameter flag setting.
The novel ingredients in this paper include (1) establishing appropriate
discrete Calder\'on reproducing formulae in the flag setting and a version of
the Plancherel--P\'olya inequalities for flag quadratic forms; (2) introducing
the maximal function and area function via flag Poisson kernels and flag
version of harmonic functions; (3) developing an atomic decomposition via the
finite speed propagation and area function in terms of flag heat semigroups. As
a consequence of these real variable methods, we obtain the full
characterisations of the multi-parameter Hardy space with the flag structure.
-
Given an ideal I on ω, we prove that a sequence in a
topological space X is I-convergent if and only if there exists a
``big'' I-convergent subsequence. Then, we study several properties
and show two characterizations of the set of I-cluster points as
classical cluster points of a filters on X and as the smallest closed set
containing ``almost all'' the sequence. As a consequence, we obtain that the
underlying topology τ coincides with the topology generated by the pair
(τ,I).
-
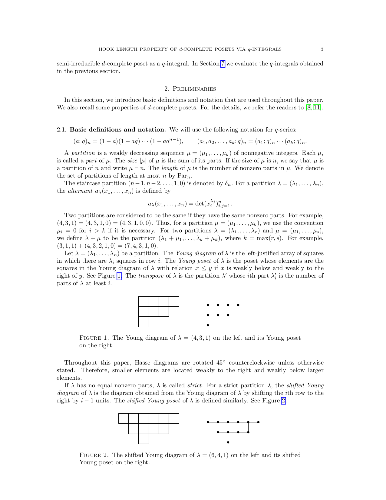
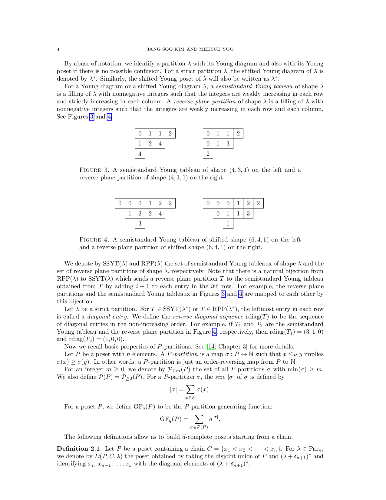
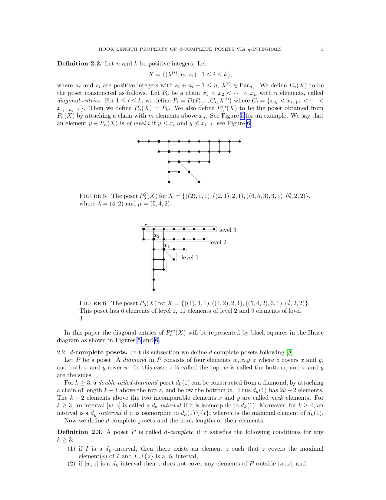
The hook length formula for d-complete posets states that the P-partition
generating function for them is given by a product in terms of hook lengths. We
give a new proof of the hook length formula using q-integrals. The proof is
done by a case-by-case analysis consisting of two steps. First, we express the
P-partition generating function for each case as a q-integral and then we
evaluate the q-integrals. Several q-integrals are evaluated using partial
fraction expansion identities and others are verified by computer.
-
We give a survey of elliptic hypergeometric functions associated with root
systems, comprised of three main parts. The first two form in essence an
annotated table of the main evaluation and transformation formulas for elliptic
hypergeometric integeral and series on root systems. The third and final part
gives an introduction to Rains' elliptic Macdonald-Koornwinder theory (in part
also developed by Coskun and Gustafson).