-
We introduce a novel class of credit risk models in which the drift of the
survival process of a firm is a linear function of the factors. The prices of
defaultable bonds and credit default swaps (CDS) are linear-rational in the
factors. The price of a CDS option can be uniformly approximated by polynomials
in the factors. Multi-name models can produce simultaneous defaults, generate
positively as well as negatively correlated default intensities, and
accommodate stochastic interest rates. A calibration study illustrates the
versatility of these models by fitting CDS spread time series. A numerical
analysis validates the efficiency of the option price approximation method.
-
The determination of acceptability prices of contingent claims requires the
choice of a stochastic model for the underlying asset price dynamics. Given
this model, optimal bid and ask prices can be found by stochastic optimization.
However, the model for the underlying asset price process is typically based on
data and found by a statistical estimation procedure. We define a confidence
set of possible estimated models by a nonparametric neighborhood of a baseline
model. This neighborhood serves as ambiguity set for a multi-stage stochastic
optimization problem under model uncertainty. We obtain distributionally robust
solutions of the acceptability pricing problem and derive the dual problem
formulation. Moreover, we prove a general large deviations result for the
nested distance, which allows to relate the bid and ask prices under model
ambiguity to the quality of the observed data.
-
We consider the valuation of contingent claims with delayed dynamics in a
Black \& Scholes complete market model. We find a pricing formula that can be
decomposed into terms reflecting the market values of the past and the present,
showing how the valuation of future cashflows cannot abstract away from the
contribution of the past. As a practical application, we provide an explicit
expression for the market value of human capital in a setting with wage
rigidity.
-
We study the small-time behaviour of the rough Bergomi model, introduced by
Bayer, Friz and Gatheral (2016), and prove a large deviations principle for a
rescaled version of the normalised log stock price process, which then allows
us to characterise the small-time behaviour of the implied volatility.
-
We propose a randomised version of the Heston model-a widely used stochastic
volatility model in mathematical finance-assuming that the starting point of
the variance process is a random variable. In such a system, we study the
small-and large-time behaviours of the implied volatility, and show that the
proposed randomisation generates a short-maturity smile much steeper (`with
explosion') than in the standard Heston model, thereby palliating the
deficiency of classical stochastic volatility models in short time. We
precisely quantify the speed of explosion of the smile for short maturities in
terms of the right tail of the initial distribution, and in particular show
that an explosion rate of~tγ (γ∈[0,1/2]) for the squared
implied volatility--as observed on market data--can be obtained by a suitable
choice of randomisation. The proofs are based on large deviations techniques
and the theory of regular variations.
-
The Multi Variate Mixture Dynamics model is a tractable, dynamical,
arbitrage-free multivariate model characterized by transparency on the
dependence structure, since closed form formulae for terminal correlations,
average correlations and copula function are available. It also allows for
complete decorrelation between assets and instantaneous variances. Each single
asset is modelled according to a lognormal mixture dynamics model, and this
univariate version is widely used in the industry due to its flexibility and
accuracy. The same property holds for the multivariate process of all assets,
whose density is a mixture of multivariate basic densities. This allows for
consistency of single asset and index/portfolio smile. In this paper, we
generalize the MVMD model by introducing shifted dynamics and we propose a
definition of implied correlation under this model. We investigate whether the
model is able to consistently reproduce the implied volatility of FX cross
rates once the single components are calibrated to univariate shifted lognormal
mixture dynamics models. We consider in particular the case of the Chinese
renminbi FX rate, showing that the shifted MVMD model correctly recovers the
CNY/EUR smile given the EUR/USD smile and the USD/CNY smile, thus highlighting
that the model can also work as an arbitrage free volatility smile
extrapolation tool for cross currencies that may not be liquid or fully
observable. We compare the performance of the shifted MVMD model in terms of
implied correlation with those of the shifted Simply Correlated Mixture
Dynamics model where the dynamics of the single assets are connected naively by
introducing correlation among their Brownian motions. Finally, we introduce a
model with uncertain volatilities and correlation. The Markovian projection of
this model is a generalization of the shifted MVMD model.
-
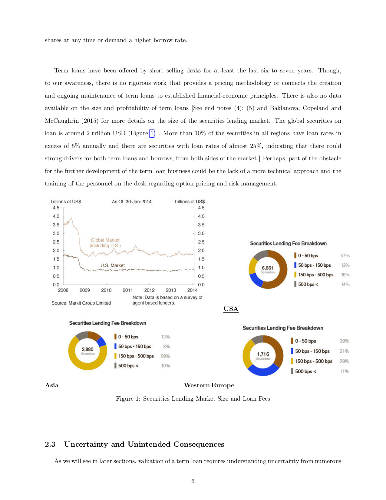
We develop models to price long term loans in the securities lending
business. These longer horizon deals can be viewed as contracts with
optionality embedded in them and can be priced using established methods from
derivatives theory, becoming to our limited knowledge, the first application
that can lead to greater synergies between the operations of derivative and
delta-one trading desks, perhaps even being able to combine certain aspects of
the day to day operations of these seemingly disparate entities. We run
numerical simulations to demonstrate the practical applicability of these
models. These models are part of one of the least explored yet profit laden
areas of modern investment management.
We develop a heuristic that can mitigate the loss of information that sets in
when parameters are estimated first and then the valuation is performed by
directly calculating the valuation using the historical time series. This can
lead to reduced models errors and greater financial stability. We illustrate
how the methodologies developed here could be useful for inventory management.
All these techniques could have applications for dealing with other financial
instruments, non-financial commodities and many forms of uncertainty. An
unintended consequence of our efforts, has become a review of the vast
literature on options pricing, which can be useful for anyone that attempts to
apply the corresponding techniques to the problems mentioned here.
Admittedly, our initial ambitions to produce a normative theory on long term
loan valuations are undone by the present state of affairs in social science
modeling. Though we consider many elements of a securities lending system at
face value, this cannot be termed a positive theory. For now, if it ends up
producing a useful theory, our work is done.
-
We derive valuations of a portfolio of financial instruments from a
securities lending perspective, under different assumptions, and show a
weighting scheme that converges to the true valuation. We illustrate conditions
under which our alternative weighting scheme converges faster to the true
valuation when compared to the minimum variance weighting. This weighting
scheme is applicable in any situation where multiple forecasts are made and we
need a methodology to combine them. Our valuations can be useful either to
derive a bidding strategy for an exclusive auction or to design an appropriate
auction mechanism, depending on which side of the fence a participant sits
(whether the interest is to procure the rights to use a portfolio for making
stock loans such as for a lending desk, or, to obtain additional revenue from a
portfolio such as from the point of view of a long only asset management firm).
Lastly, we run simulations to establish numerical examples for the set of
valuations and for various bidding strategies corresponding to different
auction settings.
-
This paper proposes to model asset price dynamics with a mixture of diffusion
processes where the instantaneous volatility of the underlying diffusion
process contains a random vector. The marginal probability distributions of the
proposed process can match exactly the risk-neutral distributions implied by
both spot vanilla options and forward start options. We can also derive the
explicit pricing formula for derivatives that have a closed-form solution under
Generalized Geometric Brownian Motion.
-
Game contingent claims (GCCs) generalize American contingent claims by
allowing the writer to recall the option as long as it is not exercised, at the
price of paying some penalty. In incomplete markets, an appealing approach is
to analyze GCCs like their European and American counterparts by solving option
holder's and writer's optimal investment problems in the underlying securities.
By this, partial hedging opportunities are taken into account. We extend
results in the literature by solving the stochastic game corresponding to GCCs
with both continuous time stopping and trading. Namely, we construct Nash
equilibria by rewriting the game as a non-zero-sum stopping game in which
players compare payoffs in terms of their exponential utility indifference
values. As a by-product, we also obtain an existence result for the optimal
exercise time of an American claim under utility indifference valuation by
relating it to the corresponding nonlinear Snell envelope.
-
Conditions of Stability for explicit finite difference scheme and some
results of numerical analysis for a unified 2 factor model of structural and
reduced form types for corporate bonds with fixed discrete coupon are provided.
It seems to be difficult to get solution formula for PDE model which
generalizes Agliardi's structural model [1] for discrete coupon bonds into a
unified 2 factor model of structural and reduced form types and we study a
numerical analysis for it by explicit finite difference scheme. These equations
are parabolic equations with 3 variables and they include mixed derivatives, so
the explicit finite difference scheme is not stable in general. We find
conditions for the explicit finite difference scheme to be stable, in the case
that it is stable, numerically compute the price of the bond and analyze its
credit spread and duration.
-
Binomial tree methods (BTM) and explicit difference schemes (EDS) for the
variational inequality model of American options with time dependent
coefficients are studied. When volatility is time dependent, it is not
reasonable to assume that the dynamics of the underlying asset's price forms a
binomial tree if a partition of time interval with equal parts is used. A time
interval partition method that allows binomial tree dynamics of the underlying
asset's price is provided. Conditions under which the prices of American option
by BTM and EDS have the monotonic property on time variable are found. Using
convergence of EDS for variational inequality model of American options to
viscosity solution the decreasing property of the price of American put options
and increasing property of the optimal exercise boundary on time variable are
proved. First, put options are considered. Then the linear homogeneity and
call-put symmetry of the price functions in the BTM and the EDS for the
variational inequality model of American options with time dependent
coefficients are studied and using them call options are studied.
-
We introduce a regularization approach to arbitrage-free factor-model
selection. The considered model selection problem seeks to learn the closest
arbitrage-free HJM-type model to any prespecified factor-model. An asymptotic
solution to this, a priori computationally intractable, problem is represented
as the limit of a 1-parameter family of optimizers to computationally tractable
model selection tasks. Each of these simplified model-selection tasks seeks to
learn the most similar model, to the prescribed factor-model, subject to a
penalty detecting when the reference measure is a local martingale-measure for
the entire underlying financial market. A simple expression for the penalty
terms is obtained in the bond market withing the affine-term structure setting,
and it is used to formulate a deep-learning approach to arbitrage-free affine
term-structure modelling. Numerical implementations are also performed to
evaluate the performance in the bond market.
-
We show that an American put option with delivery lags can be decomposed as a
European put option and another American-style derivative. The latter is an
option for which the investor receives the Greek Theta of the corresponding
European option as the running payoff, and decides an optimal stopping time to
terminate the contract. Based on the this decomposition, we further show that
the associated optimal exercise boundary exists, and is a strictly increasing
and smooth curve. We also analyze its asymptotic behavior for both large
maturity and small time lag using the free-boundary method.
-
Contrary to the common view that exact pricing is prohibitive owing to the
curse of dimensionality, this study proposes an efficient and unified method
for pricing options under multivariate Black-Scholes-Merton (BSM) models, such
as the basket, spread, and Asian options. The option price is expressed as a
quadrature integration of analytic multi-asset BSM prices under a single
Brownian motion. Then the state space is rotated in such a way that the
quadrature requires much coarser nodes than it would otherwise or low varying
dimensions are reduced. The accuracy and efficiency of the method is
illustrated through various numerical experiments.
-
The purpose of this paper is to analyze the problem of option pricing when
the short rate follows subdiffusive fractional Merton model. We incorporate the
stochastic nature of the short rate in our option valuation model and derive
explicit formula for call and put option and discuss the corresponding
fractional Black-Scholes equation. We present some properties of this pricing
model for the cases of α and H. Moreover, the numerical simulations
illustrate that our model is flexible and easy to implement.
-
Kristensen and Mele (2011) developed a new approach to obtain closed-form
approximations to continuous-time derivatives pricing models. The approach uses
a power series expansion of the pricing bias between an intractable model and
some known auxiliary model. Since the resulting approximation formula has
closed-form it is straightforward to obtain approximations of greeks. In this
thesis I will introduce Kristensen and Mele's methods and apply it to a variety
of stochastic volatility models of European style options as well as a model
for commodity futures. The focus of this thesis is the effect of different
model choices and different model parameter values on the numerical stability
of Kristensen and Mele's approximation.
-
Emerging market hard-currency bonds are an asset class of growing importance,
and contain exposure to an EM sovereign and the underlying industry. The
authors investigate how to model this as a modification of the well-known
first-to-default (FtD) basket, using the structural model, and find the
approach feasible.
-
We characterize the price of an Asian option, a financial contract, as a
fixed-point of a non-linear operator. In recent years, there has been interest
in incorporating changes of regime into the parameters describing the evolution
of the underlying asset price, namely the interest rate and the volatility, to
model sudden exogenous events in the economy. Asian options are particularly
interesting because the payoff depends on the integrated asset price. We study
the case of both floating- and fixed-strike Asian call options with arithmetic
averaging when the asset follows a regime-switching geometric Brownian motion
with coefficients that depend on a Markov chain. The typical approach to
finding the value of a financial option is to solve an associated system of
coupled partial differential equations. Alternatively, we propose an iterative
procedure that converges to the value of this contract with geometric rate
using a classical fixed-point theorem.
-
Within the context of the banking-related literature on contingent
convertible bonds, we comprehensively formalise the design and features of a
relatively new type of insurance-linked security, called a contingent
convertible catastrophe bond (CocoCat). We begin with a discussion of its
design and compare its relative merits to catastrophe bonds and
catastrophe-equity puts. Subsequently, we derive analytical valuation formulae
for index-linked CocoCats under the assumption of independence between natural
catastrophe and financial markets risks. We model natural catastrophe losses by
a time-inhomogeneous compound Poisson process, with the interest-rate process
governed by the Longstaff model. By using an exponential change of measure on
the loss process, as well as a Girsanov-like transformation to synthetically
remove the correlation between the share and interest-rate processes, we obtain
these analytical formulae. Using selected parameter values in line with earlier
research, we empirically analyse our valuation formulae for index-linked
CocoCats. An analysis of the results reveals that the CocoCat prices are most
sensitive to changing interest-rates, conversion fractions and the threshold
levels defining the trigger times.
-
Contingent Convertible bonds (CoCos) are debt instruments that convert into
equity or are written down in times of distress. Existing pricing models assume
conversion triggers based on market prices and on the assumption that markets
can always observe all relevant firm information. But all Cocos issued so far
have triggers based on accounting ratios and/or regulatory intervention. We
incorporate that markets receive information through noisy accounting reports
issued at discrete time instants, which allows us to distinguish between market
and accounting values, and between automatic triggers and regulator-mandated
conversions. Our second contribution is to incorporate that coupon payments are
contingent too: their payment is conditional on the Maximum Distributable
Amount not being exceeded. We examine the impact of CoCo design parameters,
asset volatility and accounting noise on the price of a CoCo; and investigate
the interaction between CoCo design features, the capital structure of the
issuing bank and their implications for risk taking and investment incentives.
Finally, we use our model to explain the crash in CoCo prices after Deutsche
Bank's profit warning in February 2016.
-
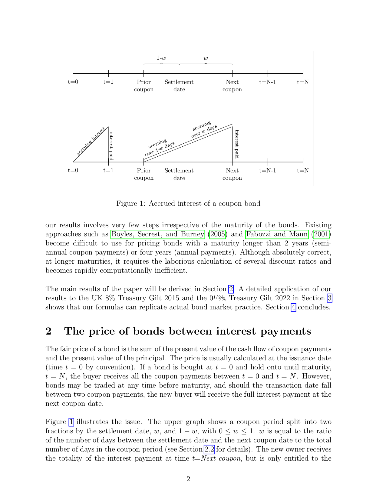
We derive a closed-form formula for computing bond prices between coupon
payments. Our results cover both the `Treasury' and the `Street' pricing
methods used by sovereign and corporate issuers. We apply our formulas to two
UK gilts, the 8% Treasury Gilt 2015, and the 0.5% Treasury Gilt 2022, and show
that we can obtain the dirty price of these bonds at any date with a minimum of
calculations, and without intensive computational resources.
-
Recent empirical studies suggest that the volatilities associated with
financial time series exhibit short-range correlations. This entails that the
volatility process is very rough and its autocorrelation exhibits sharp decay
at the origin. Another classic stylistic feature often assumed for the
volatility is that it is mean reverting. In this paper it is shown that the
price impact of a rapidly mean reverting rough volatility model coincides with
that associated with fast mean reverting Markov stochastic volatility models.
This reconciles the empirical observation of rough volatility paths with the
good fit of the implied volatility surface to models of fast mean reverting
Markov volatilities. Moreover, the result conforms with recent numerical
results regarding rough stochastic volatility models. It extends the scope of
models for which the asymptotic results of fast mean reverting Markov
volatilities are valid. The paper concludes with a general discussion of
fractional volatility asymptotics and their interrelation. The regimes
discussed there include fast and slow volatility factors with strong or small
volatility fluctuations and with the limits not commuting in general. The
notion of a characteristic term structure exponent is introduced, this exponent
governs the implied volatility term structure in the various asymptotic
regimes.
-
Recent empirical studies suggest that the volatility of an underlying price
process may have correlations that decay slowly under certain market
conditions. In this paper, the volatility is modeled as a stationary process
with long-range correlation properties in order to capture such a situation,
and we consider European option pricing. This means that the volatility process
is neither a Markov process nor a martingale. However, by exploiting the fact
that the price process is still a semimartingale and accordingly using the
martingale method, we can obtain an analytical expression for the option price
in the regime where the volatility process is fast mean-reverting. The
volatility process is modeled as a smooth and bounded function of a fractional
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process. We give the expression for the implied volatility,
which has a fractional term structure.
-
We describe a robust calibration algorithm of a set of SSVI slices (i.e. a
set of 3 SSVI parameters θ,ρ,φ attached to each option
maturity available on the market), which grants that these slices are free of
Butterfly and Calendar-Spread arbitrage. Given such a set of consistent SSVI
parameters, we show that the most natural interpolation/extrapolation of the
parameters provides a full continuous volatility surface free of arbitrage. The
numerical implementation is straightforward, robust and quick, yielding an
effective, parsimonious solution to the smile problem, which has the potential
to become a benchmark one.