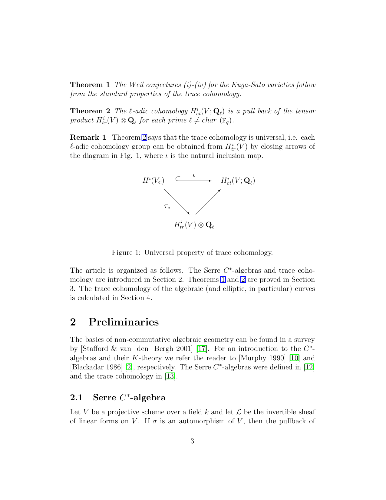
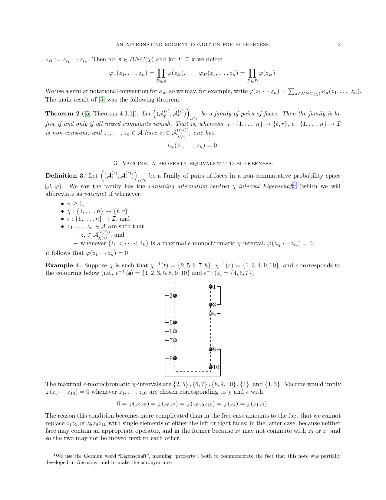
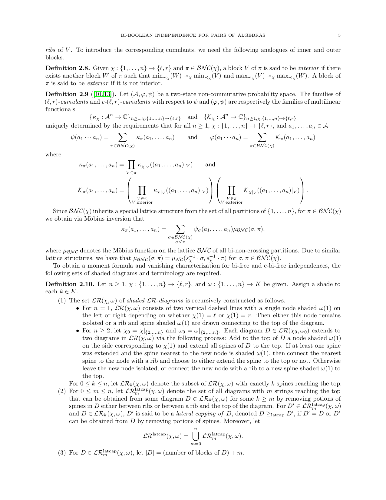
-
A C*-dynamical system is said to have the ideal separation property if every
ideal in the corresponding crossed product arises from an invariant ideal in
the C*-algebra. In this paper we characterize this property for unital
C*-dynamical systems over discrete groups. To every C*-dynamical system we
associate a "twisted" partial C*-dynamical system that encodes much of the
structure of the action. This system can often be "untwisted," for example when
the algebra is commutative, or when the algebra is prime and a certain specific
subgroup has vanishing Mackey obstruction. In this case, we obtain relatively
simple necessary and sufficient conditions for the ideal separation property. A
key idea is a notion of noncommutative boundary for a C*-dynamical system that
generalizes Furstenberg's notion of topological boundary for a group.
-
This article proves that an irreducible subfactor planar algebra with a
distributive biprojection lattice admits a minimal 2-box projection generating
the identity biprojection. It is a generalization (conjectured in 2013) of a
theorem of Oystein Ore on distributive intervals of finite groups (1938), and a
corollary of a natural subfactor extension of a conjecture of Kenneth S. Brown
in algebraic combinatorics (2000). We deduce a link between combinatorics and
representations in finite group theory.
-
If matrices almost satisfying a group relation are close to matrices exactly
satisfying the relation, then we say that a group is matricially stable. Here
"almost" and "close" are in terms of the Hilbert-Schmidt norm. Using tracial
2-norm on $II_1$-factors we similarly define $II_1$-factor stability for
groups. Our main result is that all 1-relator groups with non-trivial center
are $II_{1}$-factor stable. Many of them are also matricially stable and RFD.
For amenable groups we give a complete characterization of matricial stability
in terms of the following approximation property for characters: each character
must be a pointwise limit of traces of finite-dimensional representations. This
allows us to prove matricial stability for the discrete Heisenberg group
$\mathbb H_3$ and for all virtually abelian groups. For non-amenable groups the
same approximation property is a necessary condition for being matricially
stable. We study this approximation property and show that RF groups with
character rigidity have it.
-
Let $A$ be a non-commutative, non-unital $\mathrm{C}^\ast$-algebra. Given a
set of commuting positive elements in the corona algebra $Q(A)$, we study some
obstructions to the existence of a commutative lifting of such set to the
multiplier algebra $M(A)$. Our focus are the obstructions caused by the size of
the collection we want to lift. It is known that no obstacles show up when
lifting a countable family of commuting projections, or of pairwise orthogonal
positive elements. However, this is not the case for larger collections. We
prove in fact that for every primitive, non-unital, $\sigma$-unital
$\mathrm{C}^\ast$-algebra $A$, there exists an uncountable set of pairwise
orthogonal positive elements in $Q(A)$ such that no uncountable subset of it
can be lifted to a set of commuting elements of $M(A)$. Moreover, the positive
elements in $Q(A)$ can be chosen to be projections if $A$ has real rank zero.
-
We use a cohomology theory coming from the canonical trace on a C*-algebra of
the projective variety to prove an analog of the Riemann Hypothesis for the
Kuga-Sato varieties over finite fields.
-
The theory of quasifree quantum stochastic calculus for infinite-dimensional
noise is developed within the framework of Hudson-Parthasarathy quantum
stochastic calculus. The question of uniqueness for the covariance amplitude
with respect to which a given unitary quantum stochastic cocycle is quasifree
is addressed, and related to the minimality of the corresponding stochastic
dilation. The theory is applied to the identification of a wide class of
quantum random walks whose limit processes are driven by quasifree noises.
-
We present a general theory of braided quantum groups in the C*-algebraic
framework using the language of multiplicative unitaries. Starting with a
manageable multiplicative unitary in the representation category of the quantum
codouble of a regular quantum group $\mathbb{G}$ we construct a braided
C*-quantum group over $\mathbb{G}$ as a C*-bialgebra in the monoidal category
of the $\mathbb{G}$-Yetter-Drinfeld C*-algebras. Furthermore, we establish the
one to one correspondence between braided C*-quantum groups and C*-quantum
groups with projection. Consequently, we generalise the bosonization
construction for braided Hopf-algebras of Radford and Majid to braided
C*-quantum groups. Several examples are discussed. In particular, we show that
the complex quantum plane admits a the braided C*-quantum group structure over
the circle group $\mathbb{T}$ and identify its bosonization with the simplified
quantum $E(2)$ group.
-
The objective of this series is to study metric geometric properties of
(coarse) disjoint unions of amenable Cayley graphs. We employ the Cayley
topology and observe connections between large scale structure of metric spaces
and group properties of Cayley accumulation points. In this Part I, we prove
that a disjoint union has property A of G. Yu if and only if all groups
appearing as Cayley accumulation points in the space of marked groups are
amenable. As an application, we construct two disjoint unions of finite special
linear groups (and unimodular linear groups) with respect to two systems of
generators that look similar such that one has property A and the other does
not admit (fibred) coarse embeddings into any Banach space with non-trivial
type (for instance, any uniformly convex Banach space).
-
We construct uncountably many mutually nonisomorphic simple separable stably
finite unital exact C$^\ast$-algebras which are not isomorphic to their
opposite algebras. In particular, we prove that there are uncountably many
possibilities for the $K_0$-group, the $K_1$-group, and the tracial state space
of such an algebra. We show that these C*-algebras satisfy the Universal
Coefficient Theorem. This is new even for the already known example of an exact
C*-algebra nonisomorphic to its opposite algebra produced in earlier work.
-
We continue our study of the outer Pinsker factor for probability
measure-preserving actions of sofic groups. Using the notion of doubly quenched
convergence developed by Austin, we prove that in many cases the outer Pinsker
factor of a product action is the product of the outer Pinsker factors. Our
results are parallel to those of Seward for Rohklin entropy. We use these
Pinsker products formulas to show that for many actions of a sofic group G on X
where X is a compact group and the action is by automorphism, the (measurable)
outer Pinsker factor of the action of G on X is given as a quotient by a
G-invariant, closed, normal subgroup. We use our results to show that if G is
sofic and f in M_{n}(Z(G)) is invertible as a convolution operator, then the
action of G on the Pontryagin dual of \Z(G)^{\oplus n}/\Z(G)^{\oplus n}f has
completely positive measure-theoretic entropy with respect to the Haar measure.
This last application requires our previous work connecting topological entropy
in the presence as defined by Li-Liang to measure-theoretic entropy in the
presence (implicitly defined by Kerr) for actions on compact groups. In
particular, we need our previous formulation of measure-theoretic entropy in
the presence in terms of a given topological model.
-
In this paper, we study the partial bi-free $S$-transform of a pair $(a,b)$
of random variables, and the $S$-transform of the $2\times 2$ matrix-valued
random variable $\left(\begin{matrix}a&0\\0&b\end{matrix}\right)$ associated
with $(a,b)$ when restricted to upper triangular $2\times 2$ matrices. We first
derive an explicit expression of bi-free multiplicative convolution (of
probability measures on the bi-unit-sphere $\mathbb{T}^2$ of $\mathbb{C}^2$, or
on $\mathbb{R}^2_+$ in $\mathbb{C}^2$) from a subordination equation for
bi-free multiplicative convolution. We then show that, when $(a_1, b_1)$ and
$(a_2,b_2)$ are bi-free, the $S$-transforms of
$X_1=\left(\begin{matrix}a_1&0\\0&b_1\end{matrix}\right)$,
$X_2=\left(\begin{matrix}a_2&0\\0&b_2\end{matrix}\right)$ satisfy Dykema's
twisted multiplicative equation for free operator-valued random variables if
and only if at least one of the two partial bi-free $S$-transforms of the pairs
of random variables is the constant function 1 in a neighborhood of $(0,0)$.
This is the case if and only if one of the two pairs, say $(a_1,b_1)$, has
factoring two-band moments (that is,
$\varphi(a_1^mb_1^n)=\varphi(a_1^m)\varphi(b_1^n)$, for all $m,n=1, 2,
\cdots$). We thus find tons of bi-free pairs of random variables to which the
$S$-transforms of the corresponding matrix-value random variables do not
satisfy Dykema's twisted multiplicative formula. Finally, if both $(a_1,b_1)$
and $(a_2,b_2)$ have factoring two-band moments, we prove that the
$\Psi$-transforms of $X_1$, $X_2$, and $X_1X_2$ satisfy a subordination
equation.
-
Alain Connes and Nigel Higson pointed out in the 1990s that the
Connes-Kasparov "conjecture"' for the K-theory of reduced groupe
$C^\ast$-algebras seemed, in the case of reductive Lie groups, to be a
cohomological echo of a conjecture of George Mackey concerning the rigidity of
representation theory along the deformation from a reductive Lie group to its
Cartan motion group. For complex semisimple groups, Nigel Higson established in
2008 that Mackey's analogy is a real phenomenon and does lead to a simple proof
of the Connes-Kasparov isomorphism. We here turn to more general reductive
groups and use our recent work on Mackey's proposal, together with Higson's
work, to obtain a new proof of the Connes-Kasparov isomorphism.
-
Let $(X,T,\mu)$ be a Cantor minimal sytem and $[[T]]$ the associated
topological full group. We analyze $C^*_\pi([[T]])$, where $\pi$ is the Koopman
representation attached to the action of $[[T]]$ on $(X,\mu)$.
Specifically, we show that $C^*_\pi([[T]])=C^*_\pi([[T]]')$ and that the
kernel of the character $\tau$ on $C^*_\pi([[T]])$ coming from weak containment
of the trivial representation is a hereditary $C^*$-subalgebra of
$C(X)\rtimes\mathbb{Z}$. Consequently, $\ker\tau$ is stably isomorphic to
$C(X)\rtimes\mathbb{Z}$, and $C^*_\pi([[T]]')$ is not AF.
We also prove that if $G$ is a finitely generated, elementary amenable group
and $C^ *(G)$ has real rank zero, then $G$ is finite.
-
In this paper we define K-theoretic secondary invariants attached to a Lie
groupoid $G$. The K-theory of $C^*_r(G_{ad}^0)$ (where $G_{ad}^0$ is the
adiabatic deformation $G$ restricted to the interval $[0,1)$) is the receptacle
for K-theoretic secondary invariants. We give a Lie groupoid version of
construction given by Piazza and Schick in the setting of the Coarse Geometry.
Our construction directly generalises to more involved geometrical situation,
such as foliations, well encoded by a Lie groupoid. Along the way we tackle the
problem of producing a wrong-way functoriality between adiabatic deformation
groupoid K-groups with respect to transverse maps. This extends the
construction of the lower shriek map given by Connes and Skandalis. Moreover we
attach a secondary invariant to the two following operators: the signature
operator on a pair of homotopically equivalent Lie groupoids; the Dirac
operator on a Lie groupoid equipped with a metric that has positive scalar
curvature $s$-fiber-wise. Furthermore we prove a Lie groupoid version of the
Delocalized APS Index Theorem of Piazza and Schick. Finally we give a product
formula for the secondary invariants and we state stability results about
cobordism classes of Lie groupoid structures and bordism classes of Lie
groupoid metric with positive scalar curvature along the $s$-fibers.
This is the revised version accepted by Advances in Mathematics.
-
A C*-algebra is determined to a great extent by the partial order of its
commutative C*-algebras. We study order-theoretic properties of this dcpo. Many
properties coincide: the dcpo is, equivalently, algebraic, continuous,
meet-continuous, atomistic, quasi-algebraic, or quasi-continuous, if and only
if the C*-algebra is scattered. For C*-algebras with enough projections, these
properties are equivalent to finite-dimensionality. Approximately
finite-dimensional elements of the dcpo correspond to Boolean subalgebras of
the projections of the C*-algebra, which determine the projections up to
isomorphism. Scattered C*-algebras are finite-dimensional if and only if their
dcpo is Lawson-scattered. General C*-algebras are finite-dimensional if and
only if their dcpo is order-scattered.
-
We define the standard Borel space of free Araki-Woods factors and prove that
their isomorphism relation is not classifiable by countable structures. We also
prove that equality of $\tau$-topologies, arising as invariants of type III
factors, as well as coycle and outer conjugacy of actions of abelian groups on
free product factors are not classifiable by countable structures.
-
Let a discrete group $G$ act on a unital simple C$^*$-algebra $A$ by outer
automorphisms. We establish a Galois correspondence $H\mapsto
A\rtimes_{\alpha,r}H$ between subgroups of $G$ and C$^*$-algebras $B$
satisfying $A\subseteq B \subseteq A\rtimes_{\alpha,r}G$, where
$A\rtimes_{\alpha,r}G$ denotes the reduced crossed product. For a twisted
dynamical system $(A,G,\alpha,\sigma)$, we also prove the corresponding result
for the reduced twisted crossed product $A\rtimes^\sigma_{\alpha,r}G$.
-
A simple Steinberg algebra associated to an ample Hausdorff groupoid $G$ is
algebraically purely infinite if and only if the characteristic functions of
compact open subsets of the unit space are infinite idempotents. If a simple
Steinberg algebra is algebraically purely infinite, then the reduced groupoid
$C^*$-algebra $C^*_r(G)$ is simple and purely infinite. But the Steinberg
algebra seems to small for the converse to hold. For this purpose we introduce
an intermediate $*$-algebra $B(G)$ constructed using corners $1_U C^*_r(G) 1_U$
for all compact open subsets $U$ of the unit space of the groupoid. We then
show that if $G$ is minimal and effective, then $B(G)$ is algebraically
properly infinite if and only if $C^*_r(G)$ is purely infinite simple. We apply
our results to the algebras of higher-rank graphs.
-
The (complex) Hodge-elliptic genus and its conformal field theoretic
counterpart were recently introduced by Kachru and Tripathy, refining the
traditional complex elliptic genus. We construct a different, so-called chiral
Hodge-elliptic genus, which is expected to agree with the generic conformal
field theoretic Hodge-elliptic genus, in contrast to the complex Hodge-elliptic
genus as originally defined.
For K3 surfaces X, the chiral Hodge-elliptic genus is shown to be independent
of all moduli. Moreover, employing Kapustin's results on infinite volume limits
it is shown that it agrees with the generic conformal field theoretic
Hodge-elliptic genus of K3 theories, while the complex Hodge-elliptic genus
does not. This new invariant governs part of the field content of K3 theories,
supporting the idea that all their spaces of states have a common subspace
which underlies the generic conformal field theoretic Hodge-elliptic genus, and
thereby the complex elliptic genus. Mathematically, this space is modelled by
the sheaf cohomology of the chiral de Rham complex of X. It decomposes into
irreducible representations of the N=4 superconformal algebra such that the
multiplicity spaces of all massive representations have precisely the
dimensions required in order to furnish the representation of the Mathieu group
M24 that is predicted by Mathieu Moonshine. This is interpreted as evidence in
favour of the ideas of symmetry surfing, which have been proposed by Taormina
and the author, along with the claim that the sheaf cohomology of the chiral de
Rham complex is a natural home for Mathieu Moonshine.
These investigations also imply that the generic chiral algebra of K3
theories is precisely the N=4 superconformal algebra at central charge c=6, if
the usual predictions on infinite volume limits from string theory hold true.
-
For a right-angled Coxeter system $(W,S)$ and $q>0$, let $\mathcal{M}_q$ be
the associated Hecke von Neumann algebra, which is generated by self-adjoint
operators $T_s, s \in S$ satisfying the Hecke relation $(\sqrt{q}\: T_s - q)
(\sqrt{q} \: T_s + 1) = 0$ as well as suitable commutation relations. Under the
assumption that $(W, S)$ is irreducible and $\vert S \vert \geq 3$ it was
proved by Garncarek that $\mathcal{M}_q$ is a factor (of type II$_1$) for a
range $q \in [\rho, \rho^{-1}]$ and otherwise $\mathcal{M}_q$ is the direct sum
of a II$_1$-factor and $\mathbb{C}$.
In this paper we prove (under the same natural conditions as Garncarek) that
$\mathcal{M}_q$ is non-injective, that it has the weak-$\ast$ completely
contractive approximation property and that it has the Haagerup property. In
the hyperbolic factorial case $\mathcal{M}_q$ is a strongly solid algebra and
consequently $\mathcal{M}_q$ cannot have a Cartan subalgebra. In the general
case $\mathcal{M}_q$ need not be strongly solid. However, we give examples of
non-hyperbolic right-angled Coxeter groups such that $\mathcal{M}_q$ does not
possess a Cartan subalgebra.
-
In this note we demonstrate an equivalent condition for bi-freeness, inspired
by the well-known "vanishing of alternating centred moments" condition from
free probability. We show that all products satisfying a centred condition on
maximal monochromatic \chi-intervals have vanishing moments if and only if the
family of pairs of faces they come from is bi-free, and show that similar
characterisations hold for the amalgamated and conditional settings. In
addition, we construct a bi-free unitary Brownian motion and show that
conjugation by this process asymptotically creates bi-freeness; these
considerations lead to another characterisation of bi-free independence.
-
In this paper, the notion of bi-Boolean independence for non-unital pairs of
algebras is introduced thereby extending the notion of Boolean independence to
pairs of algebras. The notion of B-$(\ell, r)$-cumulants is defined via a
bi-Boolean moment-cumulant formula over the lattice of bi-interval partitions,
and it is demonstrated that bi-Boolean independence is equivalent to the
vanishing of mixed B-$(\ell, r)$-cumulants. Furthermore, some of the simplest
bi-Boolean convolutions are considered, and a bi-Boolean partial
$\eta$-transform is constructed for the study of limit theorems and infinite
divisibility with respect to the additive bi-Boolean convolution. In
particular, a bi-Boolean L\'{e}vy-Hin\v{c}in formula is derived in perfect
analogy with the bi-free case, and some Bercovici-Pata type bijections are
provided. Additional topics considered include the additive bi-Fermi
convolution, some relations between the $(\ell, r)$- and B-$(\ell,
r)$-cumulants, and bi-Boolean independence in an amalgamated setting.
The last section of this paper also includes an errata that will be published
with this copy of the paper.
-
Let $M$ be a $\rm II_1$ factor and let $\mathcal{F}(M)$ denote the
fundamental group of $M$. In this article, we study the following property of
$M$: for arbitrary $\rm II_1$ factor $B$, we have $\mathcal{F}(M
\overline{\otimes} B)=\mathcal{F}(M)\mathcal{F}(B)$. We prove that for any
subgroup $G\leq \mathbb{R}^*_+$ which is realized as a fundamental group of a
$\rm II_1$ factor, there exists a $\rm II_1$ factor $M$ which satisfies this
property and whose fundamental group is $G$. Using this, we deduce that if $G,H
\leq \mathbb{R}^*_+$ are realized as fundamental groups of $\rm II_1$ factors
(with separable predual), then so are groups $G \cdot H$ and $G \cap H$.
-
Let $\mathbb{G}$ be a free (unitary or orthogonal) quantum group. We prove
that for any non-amenable subfactor $N\subset L^\infty(\mathbb{G})$, which is
an image of a faithful normal conditional expectation, and for any
$\sigma$-finite factor $B$, the tensor product $N \otimes B$ has no Cartan
subalgebras. This generalizes our previous work that provides the same result
when $B$ is finite. In the proof, we establish Ozawa--Popa and Popa--Vaes's
weakly compact action on the continuous core of $N \otimes B$ as the one
relative to B, by using an operator valued weight to B and the central weak
amenability of $\mathbb{G}$.
-
In previous work, we defined and studied $\Sigma^*$-modules, a class of
Hilbert $C^*$-modules over $\Sigma^*$-algebras (the latter are $C^*$-algebras
that are sequentially closed in the weak operator topology). The present work
continues this study by developing the appropriate $\Sigma^*$-algebraic
analogue of the notion of strong Morita equivalence for $C^*$-algebras. We
define strong $\Sigma^*$-Morita equivalence, prove a few characterizations,
look at the relationship with equivalence of categories of a certain type of
Hilbert space representation, study $\Sigma^*$-versions of the interior and
exterior tensor products, and prove a $\Sigma^*$-version of the
Brown-Green-Rieffel stable isomorphism theorem.